Fig. 1: Presence of key molecules of the ECS in the dura samples from TBI patients and reduced levels of endocannabinoids in human plasma and CSF.
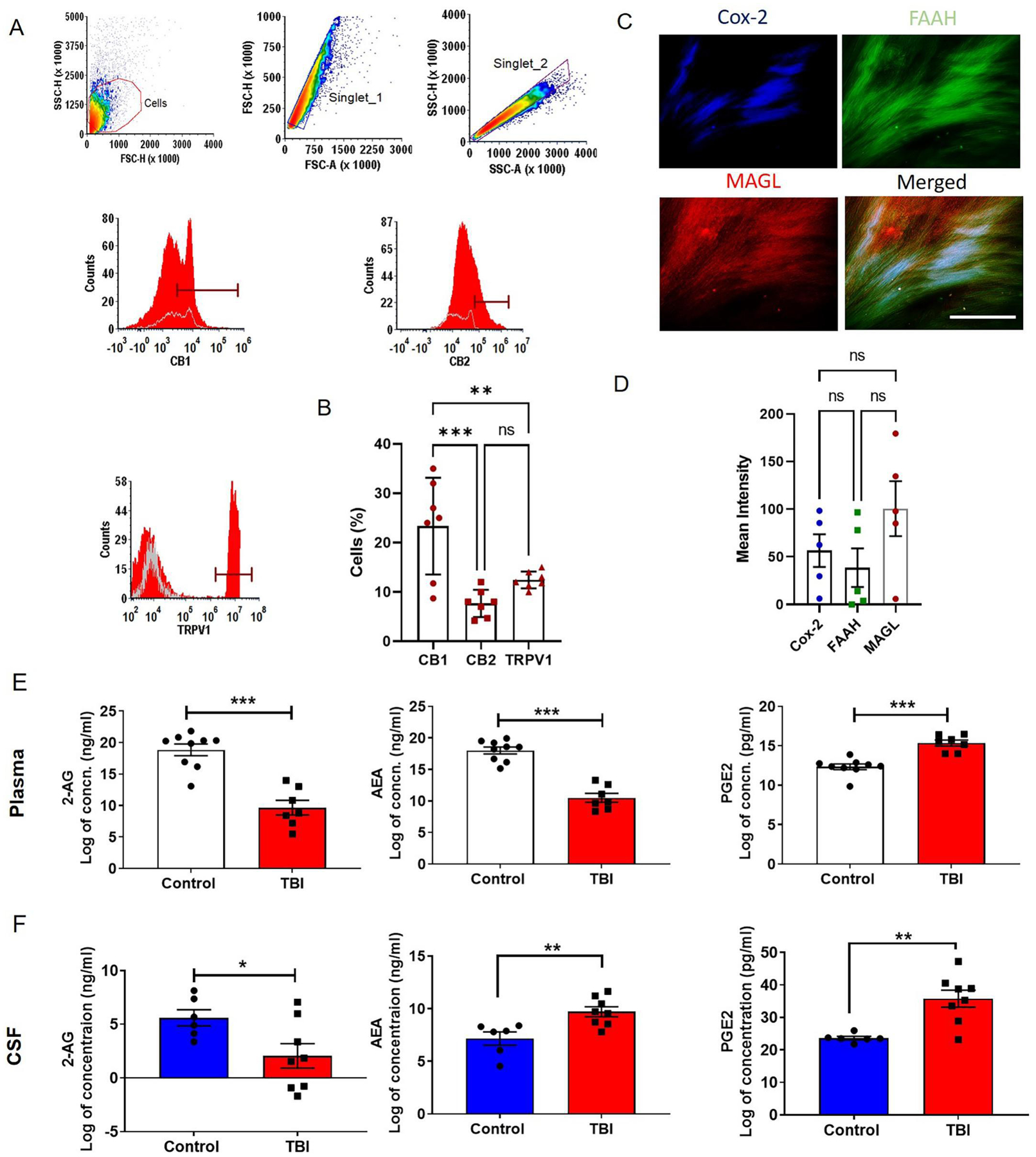
Cannabinoid and non-cannabinoid receptors were studied by flow cytometry. A and B) Our results showed the presence of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2) and non-cannabinoid receptor TRPV1 in dura from TBI patients (n = 7). The dural tissue was stained for principal cannabinoid metabolizing enzymes FAAH, MAGL and Cox-2 and mean fluorescent intensity was determined (C and D). We observed active metabolizing enzymes in dura (n = 5), suggesting a role for the ECS in brain barriers. The contents of 2-AG, AEA and PGE2 in human plasma and CSF were analyzed with the help of competitive inhibition enzyme immunoassays. Data are expressed as Log of concentrations. (E and F) Reduction in 2-AG contents was observed in TBI patient plasma and CSF. We also observed (E) low content of AEA in TBI patient plasma but, CSF from TBI victims showed a significant (F) increase in AEA level as compared with that from NPH patients. NPH patients’ spinal tap CSFs were used as controls. PGE2, an end product of endocannabinoid-arachidonic acid metabolism, acts as a pro-inflammatory mediator, was found to be elevated in both plasma and CSF (n=6–9). Two groups were compared by Paired t-test followed by Mann-Whitney test. Three groups were compared by One way ANOVA. Results were presented as mean ± SEM. Significance was ascertained as *p<0.05; **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001.
