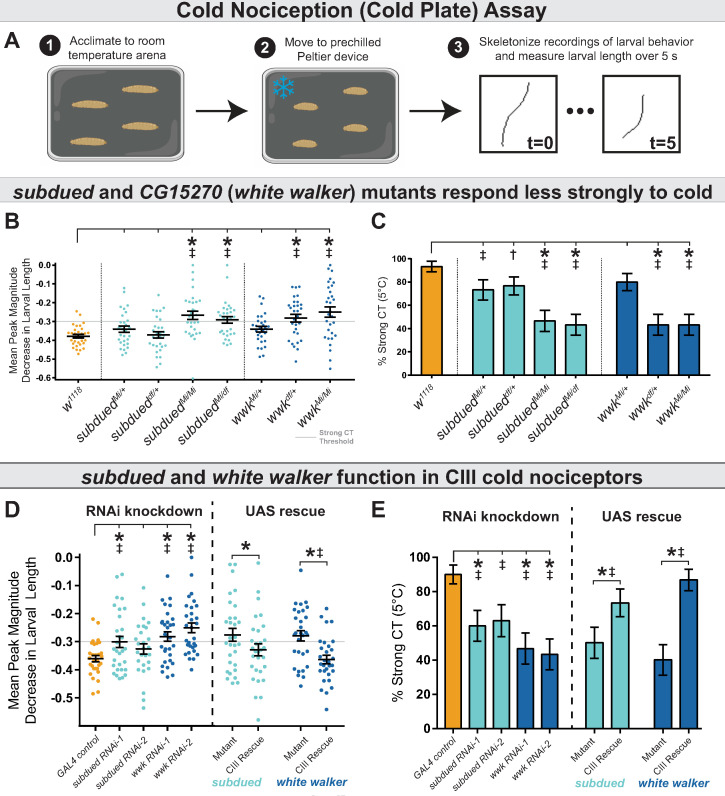
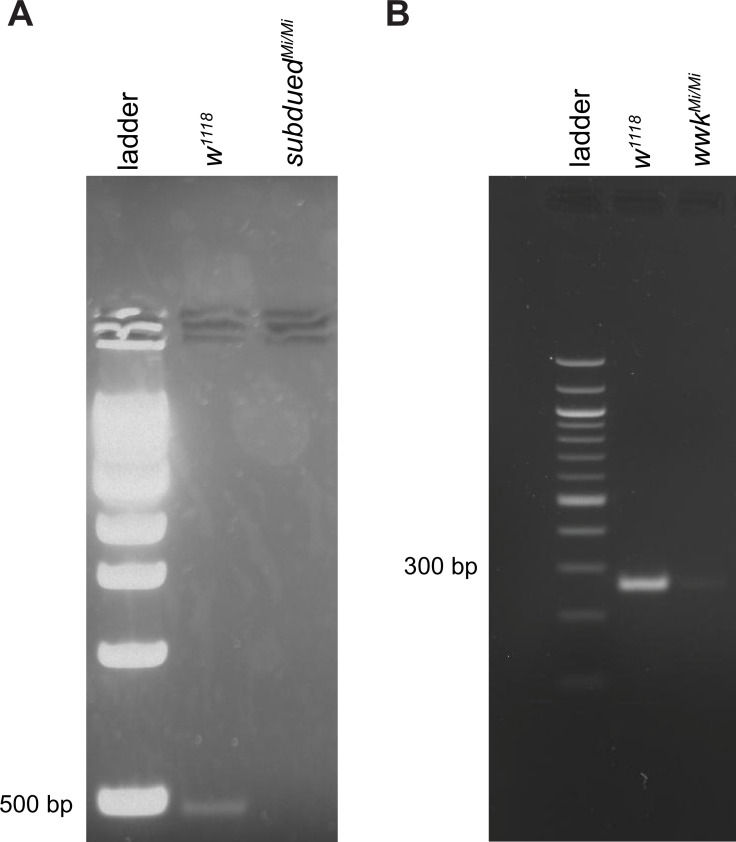
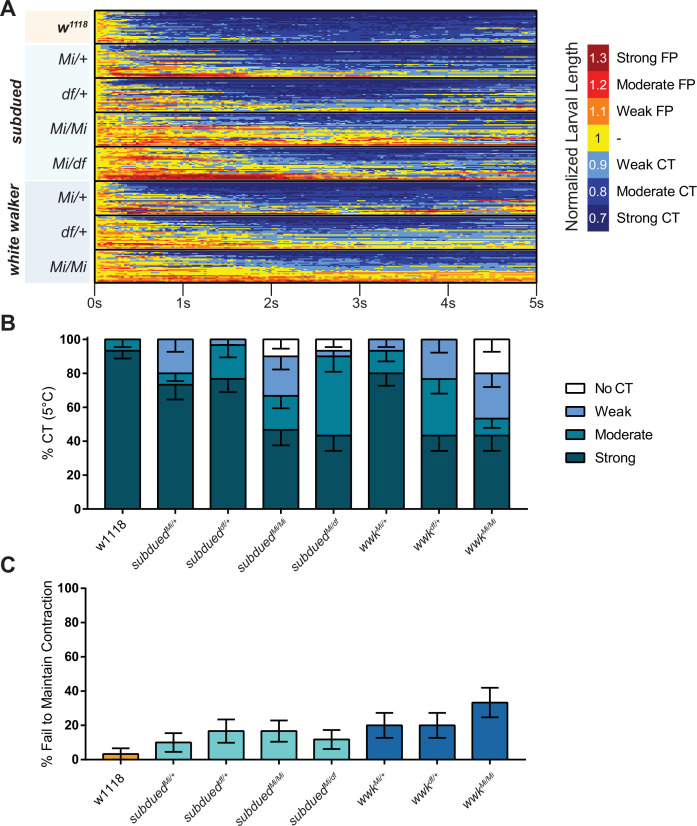
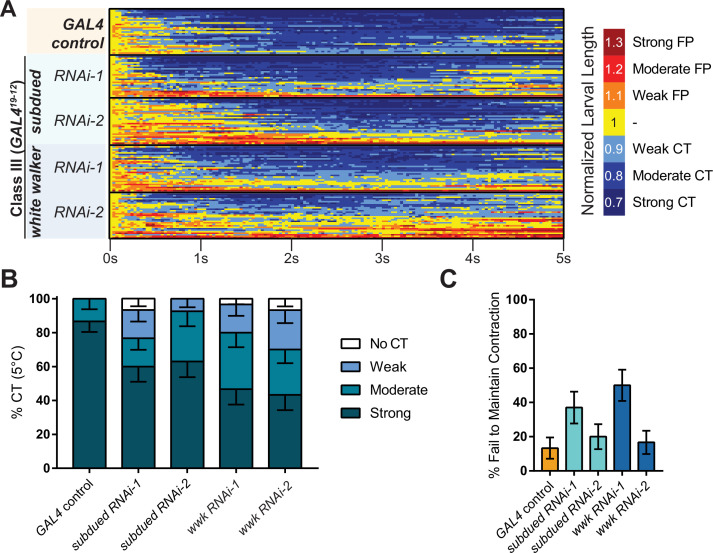
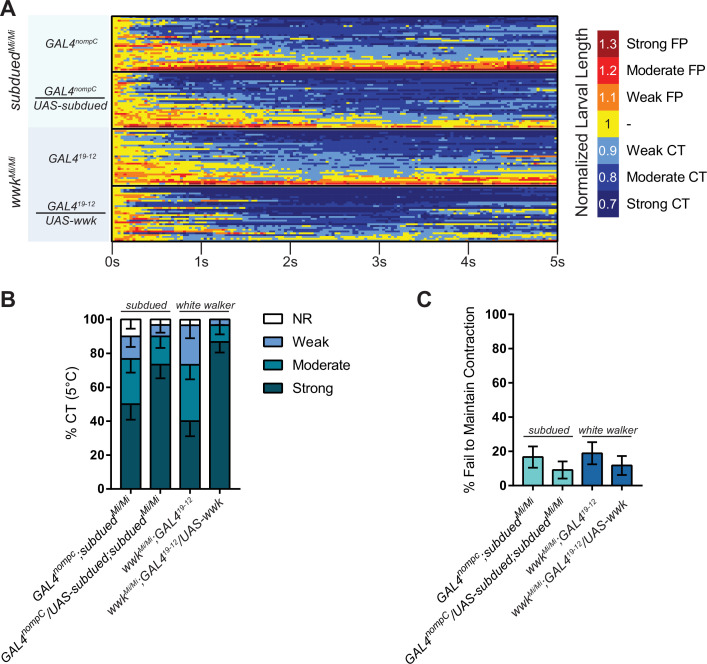
Figure 2. Anoctamins function in class III (CIII) neurons.
(A) For cold plate assay, larvae were acclimated to a room temperature arena before being transferred to a pre-chilled cold plate. Contraction (CT) was identified by measuring the length of skeletonized larvae over the course of chilling. (B) Mutant analysis; mean peak magnitude in larval CT. w1118 (n=30); subduedMi/+ (n=30; p=0.58; BF10=1.18); subdueddf/+ (n=30; p=1; BF10=0.28); subduedMi/Mi (n=30; p<0.001; BF10=228.63); subduedMi/df (n=30; p=0.008; BF10=737.03); wwkMi/+ (n=30; p=0.58; BF10=1.60); wwkdf/+ (n=30; p=0.003; BF10=324.11); wwkMi/Mi (n=30; p<0.001; BF10=433.18). Also see Figures 1—3. (C) Mutant analysis; % of animals which strongly CT in response to noxious cold (≥30% reduction in body length). Mutations in subdued and white walker result in a reduced percent of larvae which strongly CT in response to noxious cold (5°C). w1118 (n=30); subduedMi/+ (n=30; p=0.13; BF10=4.417); subdueddf/+ (n=30; p=0.25; BF10=2.826); subduedMi/Mi (n=30; p<0.001; BF10=461.34); subduedMi/df (n=30; p<0.001; BF10=997.24); wwkMi/+ (n=30; p=0.45; BF10=2.00); wwkdf/+ (n=30; p<0.001; BF10=997.24); wwkMi/Mi (n=30; p<0.001; BF10=997.24). (E) CIII-specific knockdown and rescue analyses; mean peak magnitude in larval CT. Knockdown: GAL4 control (n=30); subdued RNAi-1 (n=30; p=0.049; BF10=3.98); subdued RNAi-2 (n=27; p=0.437; BF10=0.78); wwk RNAi-1 (n=30; p=0.005; BF10=89.25); wwk RNAi-2 (n=30; p<0.001; BF10=6932.18). Rescue: GAL4nompC;subduedMi/Mi (mutant, n=30); GAL4nompC/UAS-subdued;subduedMi/Mi (CIII rescue, n=30; p=0.049; BF10=1.61). wwkMi/Mi;GAL419-12 (mutant, n=30); wwkMi/Mi;GAL419-12/UAS-wwk (CIII rescue, n=30; p<0.001; BF10=83.59). (D) CIII-specific knockdown and rescue analyses; % of animals which strongly CT in response to noxious cold (≥30% reduction in body length). CIII-specific knockdown (GAL419-12) of subdued and white walker results in a reduced percent of larvae which strongly CT in response to noxious cold. GAL4 control (n=30); subdued RNAi-1 (n=30; p=0.039; BF10=7.64); subdued RNAi-2 (n=27; p=0.075; BF10=4.93); wwk RNAi-1 (n=30; p=0.002; BF10=71.17); and wwk RNAi-2 (n=30; p<0.001; BF10=138.15). GAL4-UAS-mediated CIII rescue of subdued and white walker in mutant backgrounds increased cold sensitivity. GAL4nompC;subduedMi/Mi (n=30); GAL4nompC/UAS-subdued;subduedMi/Mi (n=30; p=0.031; BF10=3.57). wwkMi/Mi;GAL419-12 (n=30); wwkMi/Mi;GAL419-12/UAS-wwk (n=30; p<0.001; BF10=281.95).