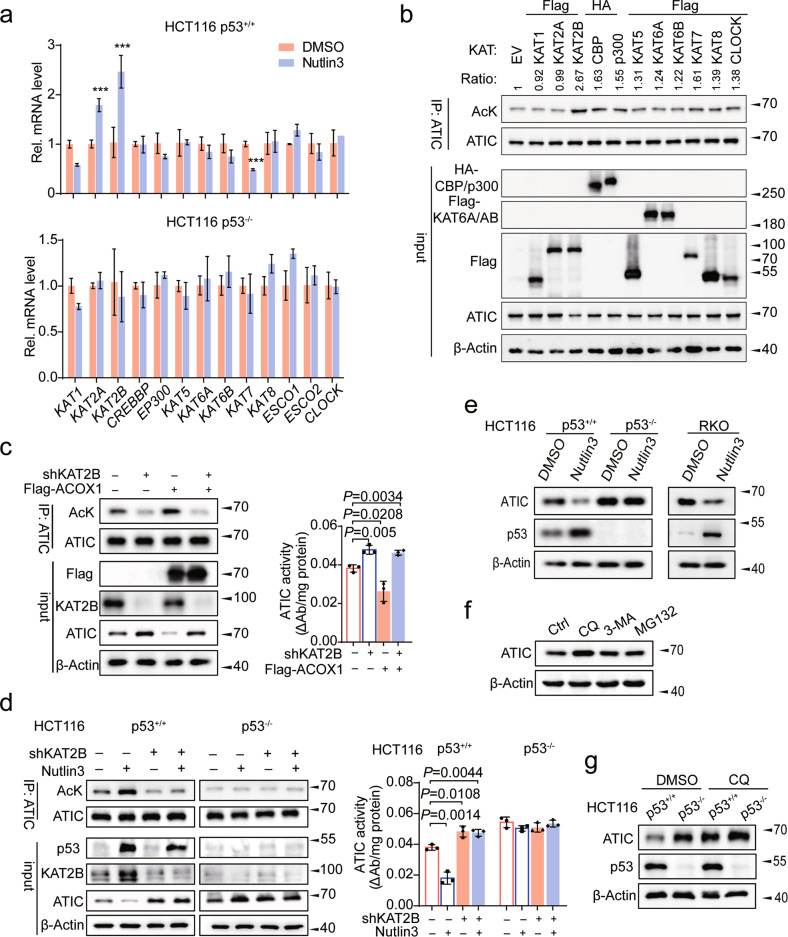
Fig. 4. p53 increases ATIC acetylation to trigger ATIC degradation by transcriptionally activating KAT2B.
a HCT116 p53+/+ and p53−/− cells were treated with either DMSO or Nutlin3 for 48 h, and the expression of 13 KAT family acetyltransferases genes were assessed by qRT-PCR, n = 3. b Western blot analysis of ATIC acetylation in HCT116 cells with overexpression of KATs. Signal intensity of Ac-ATIC protein was quantified by Image J, the acetylation level of ATIC as indicated was normalized against immunoprecipitated ATIC. c HCT116 cells expressing shCtrl or KAT2B shRNA further infected with control or Flag-ACOX1 vector, followed by western blot analysis of ATIC acetylation (left) and enzyme activity (right), n = 3. d HCT116 cells expressing shCtrl or KAT2B shRNA further treated with or without Nutlin3 for 24 h, followed by western blot analysis of ATIC acetylation (left) and enzyme activity (right), n = 3. e Protein expression of ATIC in CRC cells treated with or without Nutlin3 for 48 h. f ATIC immunoblots of lysates from HCT116 cells treated with CQ (50 μM), 3-MA (10 mM), or MG132 (10 μM) for 10 h before harvesting. g HCT116 p53+/+ and p53−/− cells treated with or without CQ (50 μM) for 10 h, followed by western blot analysis of ATIC expression. Data were presented as mean ± SD. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.