Figure 2: PD-1 deficiency increases neutrophilic AHR and lung inflammation.
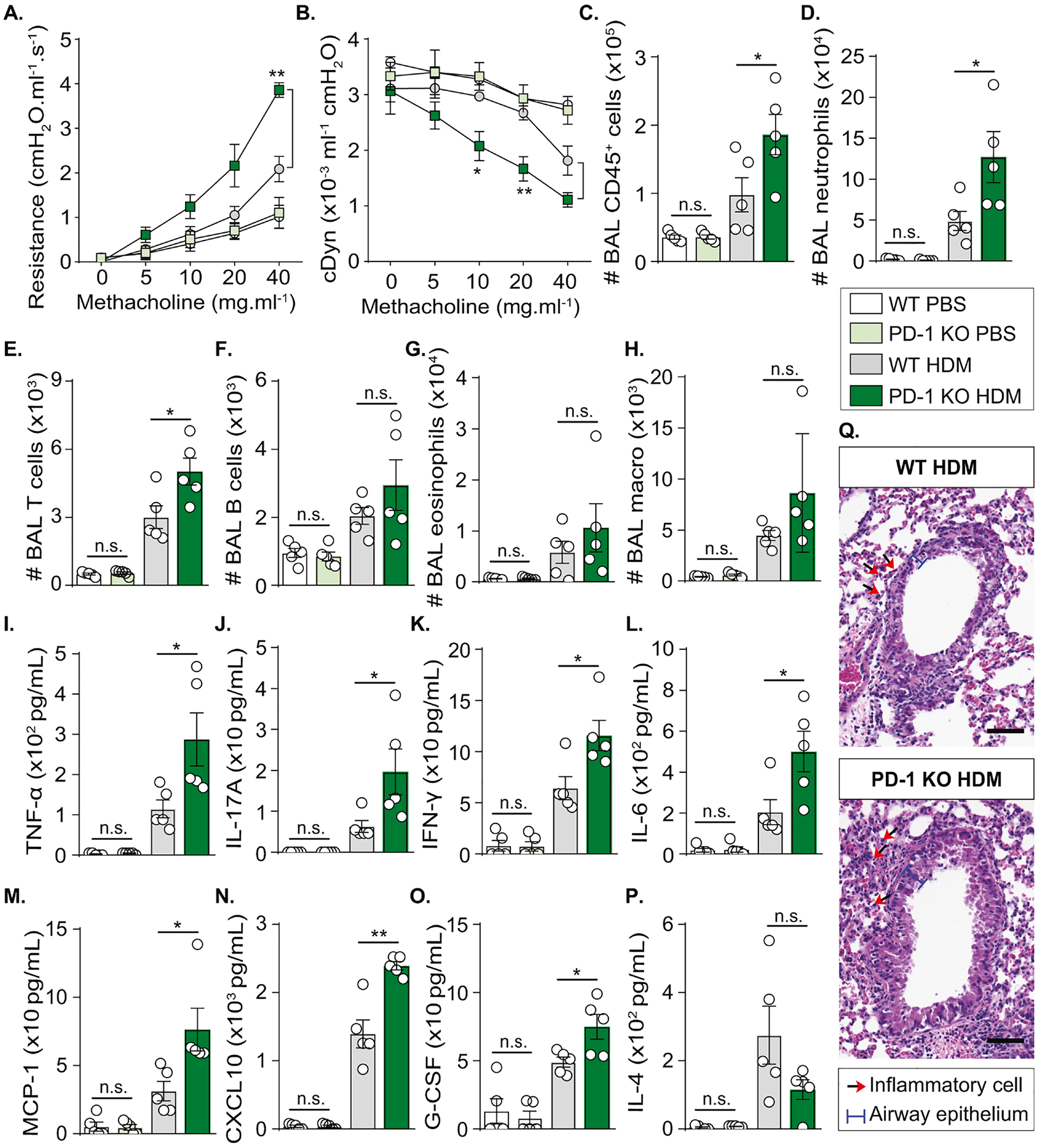
WT and PD-1 KO mice were sensitized via s.c. tail base injection of HDM (200 μg) mixed in CFA (1:1 v/v). After 13 days, mice were i.n. challenged with HDM (100 μg). Control mice received PBS only. On day 14, lung functions were measured before euthanasia and BAL collection.
(A) Lung resistance and (B) dynamic compliance measured in tracheostomized mechanically ventilated mice exposed to increasing concentrations of methacholine.
(C) Absolute count of CD45+ cells, (D) neutrophils, (E) T cells, (F) B cells, (G) eosinophils, and (H) alveolar macrophages quantified in the BAL using the count precision beads in flow cytometry analysis.
(I) Levels of TNF-α, (J) IL-17A, (K) IFN-γ, (L) IL-6, (M) MCP-1, (N) CXCL-10, (O) G-CSF, and (P) IL-4 quantified in the BAL.
(Q) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of lung sections (scale bar = 20 μm).
Data are representative of at least 2 independent experiments and are presented as means ± SEM (two-tailed Student’s t-test; n=5).
