Figure 4: PD-1 agonist downregulates AHR and controls neutrophilic lung inflammation.
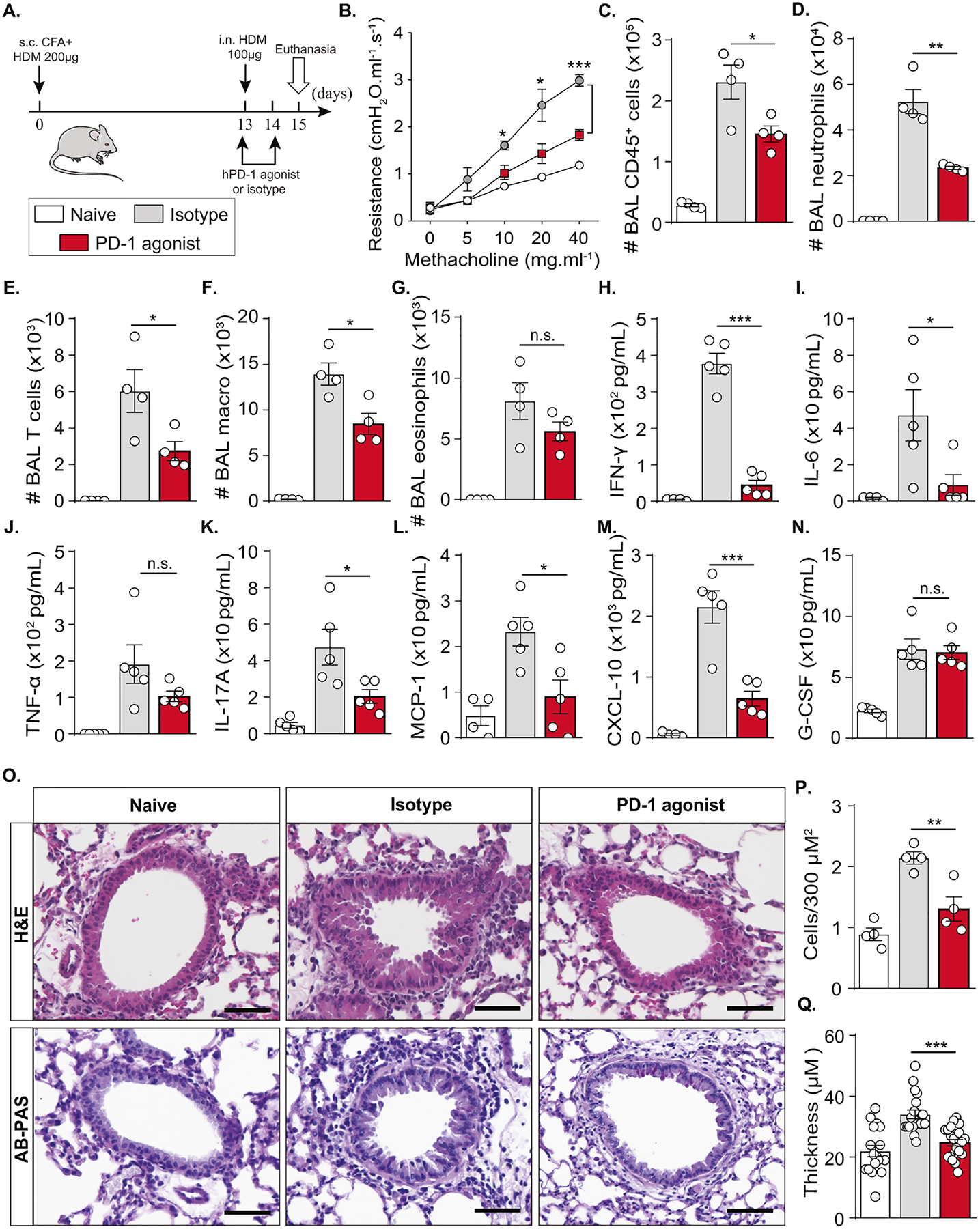
(A) Humanized PD-1 mice were sensitized via s.c. tail base injection of HDM (200 μg) mixed in CFA (1:1 v/v). After 13 days, mice were i.n. challenged with HDM (100 μg) and received 500 μg of PD-1 agonist via the intraperitoneal route or the corresponding isotype, while the dose was reduced to 250 μg via the intravenous route on day 14. Naïve mice were not sensitized, challenged, or treated. On day 15, lung function was measured. BAL and lungs were collected after euthanasia.
(B) Lung resistance measured in tracheostomized ventilated mice.
(C) Absolute count of CD45+ cells, (D) neutrophils, (E) T cells, (F) alveolar macrophages, and (G) eosinophils quantified in the BAL.
(H) Levels of IFN-γ, (I) IL-6, (J) TNF-α, (K) IL-17A, (L) MCP-1,(M) CXCL-10, and (N) G-CSF quantified in the BAL.
(O) Representative images of H&E and AB-PAS-stained histology sections (scale bar = 50 μm) with the corresponding quantifications of (P) recruited immune cells and (Q) airway epithelial thickness.
Data are representative of at least 2 independent experiments and are presented as means ± SEM (two-tailed Student’s t-test; n=4–5). Mouse image provided with permission from Servier Medical Art.
