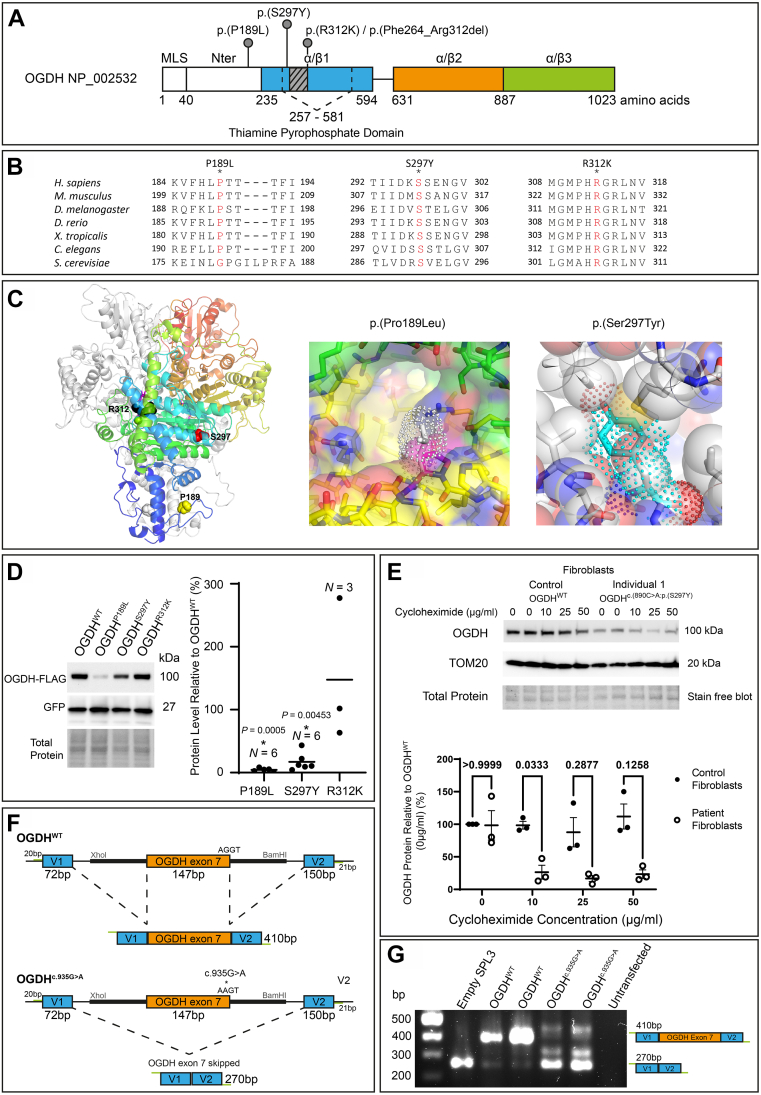
Figure 2.
OGDH protein instability or aberrant splicing demonstrated both in silico and in vitro. A. A schematic of the OGDH protein (NP_002532.2) with the TPP domain indicated alongside the OGDH variants identified in this study. The α/β1 domain is indicated in blue, α/β2 domain is indicated in orange, and α/β3 domain is indicated in green. We found that the c.935G>A p.[R312K]/p.[Phe264_Arg312del]) variant to impact splicing in our mini-gene assay (F-G), and the resulting deletion is indicated as a gray box in this schematic. In addition, the domain linker is indicated as a line between α/β1 and α/β2. The position of domains are indicated as previously reported.30 B. The OGDH variants reported alter evolutionarily conserved amino acids, as can be seen for all 3 variants. C. Homology model of the human OGDH dimer showing the location of the missense variants. Left: OGDH dimer is depicted as ribbon diagram with one monomer shown in white and the other in rainbow color from red (N-terminus) to blue (C-terminus). The bound TPP cofactor is shown as stick model (magenta) and variant sites as Corey-Pauling-Koltun model. Middle: Pro189 is located at the dimer interface. Residues surrounding Pro189Leu variant shown in yellow (cis subunit) and green (trans subunit). The bulky hydrophobic side chain of leucine substitution (white stick with dotted surface) likely destabilizes the dimer. Right: Ser297Tyr variant would cause structural clash with surrounding residues. In contrast to the serine side chain of OGDH (sphere), the tyrosine side chain of the OGDH mutant (dotted surface) would clash with neighboring atoms. D. OGDH-FLAG+GFP protein levels, detected using immunoprecipitation, in HEK293 cells transfected with either pcDNA3.1-OGDHWT-FLAG, pcDNA3.1-OGDHp.(Pro189Leu)-FLAG, pcDNA3.1-OGDHp.(Ser297Tyr)-FLAG, or pcDNA3.1-OGDHp.(Arg312Lys)-FLAG. GFP and total protein detection used for normalization. Results show a significant reduction in protein as a result of the p.(Pro189Leu) and p.(Ser297Tyr) variants. Kruskal-Wallis and a one-sample Wilcoxon test was used to statistically analyze. E. Endogenous OGDH levels detected using immunoblotting in individual 1 (p.[Ser297Tyr]) fibroblast cells and control fibroblast cells treated with cycloheximide for 24 hours at varying concentrations (0-50 μg/ml). TOM20 protein was detected and used to normalize for total mitochondrial mass within cells. OGDH level was normalized to TOM20 and analyzed as percentage change compared with control OGDH levels produced by control fibroblasts at 0 μg/mL treatment. Cycloheximide treatment revealed a higher rate of protein turnover of the OGDH protein produced by individual 1 fibroblasts than by control fibroblasts. This was significant at 10 μg/mL. P values indicated above data points. N = 3, two-way ANOVA. F, G. Results of the pSPL3 mini-gene splicing assay showing the c.935G>A variant causes whole exon skipping. F. Schematic showing the design of the pSPL3 vector. OGDH exon 7 with flanking intronic sequence indicated by the thick black line was introduced into the vector using Xhol and BamHI restriction enzyme sites. Lines indicate intronic sequence and boxes indicate exons, including the vector exons V1 and V2. OGDH exon 7 with wild-type sequence, seen above, results in accurate splicing and removal of introns. An alternative splicing pattern is shown below due to the c.935G>A variant. It results in inaccurate splicing and removal of introns as well as exon 7. Expected reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) product sizes are indicated and inclusive of primer sequences. G. HEK293 cells were transfected with the pSPL3-OGDHWT, pSPL3-OGDHc.935G>A, and empty pSPL3 vector. RNA extracts were obtained and converted to complementary DNA through RT-PCR. PCR products were amplified and visualized on a 1.5% gel. pSPL3-OGDHWT resulted in the correctly spliced product of 410 bp. pSPL3-OGDHc.935G>A did not result in the correctly spliced 410 bp but did result in a 270 bp product, showing that the c.935G>A variant results in whole exon skipping. ANOVA, analyis of variance; bp, basepair; OGDH, oxoglutarate dehydrogenase; TPP, thiamine pyrophosphate.