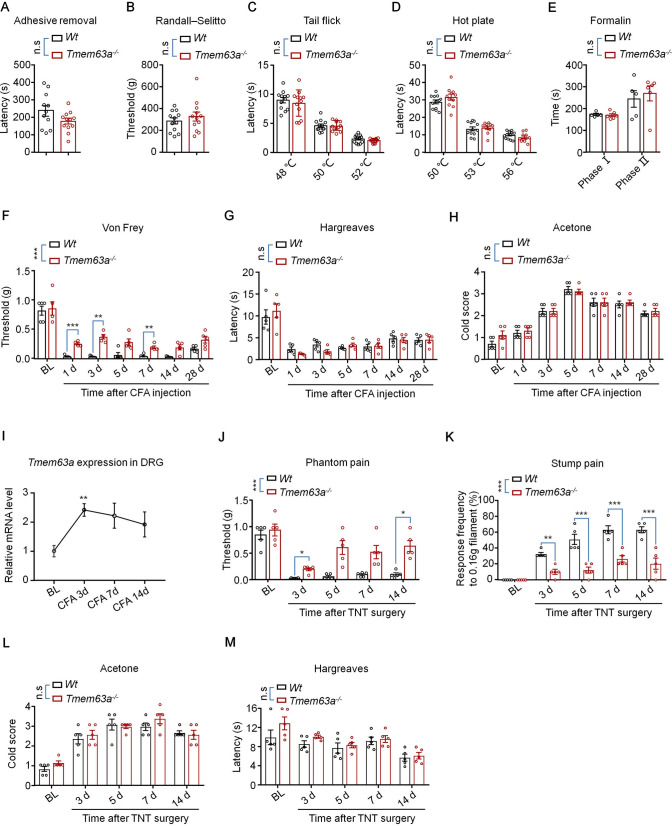
Fig. 5.
Effects of TMEM63A on touch sensation, basal pain, inflammatory pain, and CPAP. A Adhesive removal test checks the touch sensation of wild-type (WT) and Tmem63a–/– mice (n = 11–12; n.s., P >0.05, unpaired Student’s t-test). B Randall-Selitto test evaluates nociceptive responses to deep mechanical stimuli of WT and Tmem63a–/– mice (n = 12, n.s., P >0.05, unpaired Student’s t-test). C The tail flick test assays the reflex behavior of WT and Tmem63a–/– mice to heat at 48°C, 50°C, and 52°C (n = 12; n.s., P >0.05, two-way ANOVA). D The hot plate test examines the response of WT and Tmem63a–/– mice to heat at 50°C, 53°C, and 56°C (n = 11–12; n.s., P >0.05, two-way ANOVA). E Formalin test assesses the acute pain behavior of WT and Tmem63a–/– mice after intraplantar injection of formalin (n = 5–6; n.s., P >0.05, two-way ANOVA). F–H The pain hypersensitivity of WT and Tmem63a–/– mice in the CFA model: mechanical allodynia (F), heat hyperalgesia (G), and cold allodynia (H) (n = 5; n.s., P >0.05, ***P <0.001, two-way ANOVA). I qRT-PCR results for the expression of Tmem63a in the CFA mouse model (n = 3–4; **P <0.01, unpaired Student’s t-test). J–M Pain hypersensitivity of WT mice and Tmem63a–/– mice in the TNT model: phantom pain (J), stump pain (K), cold allodynia (L), and heat hyperalgesia (M) (n = 5; *P <0.05, **P <0.01, ***P <0.001, two-way ANOVA).