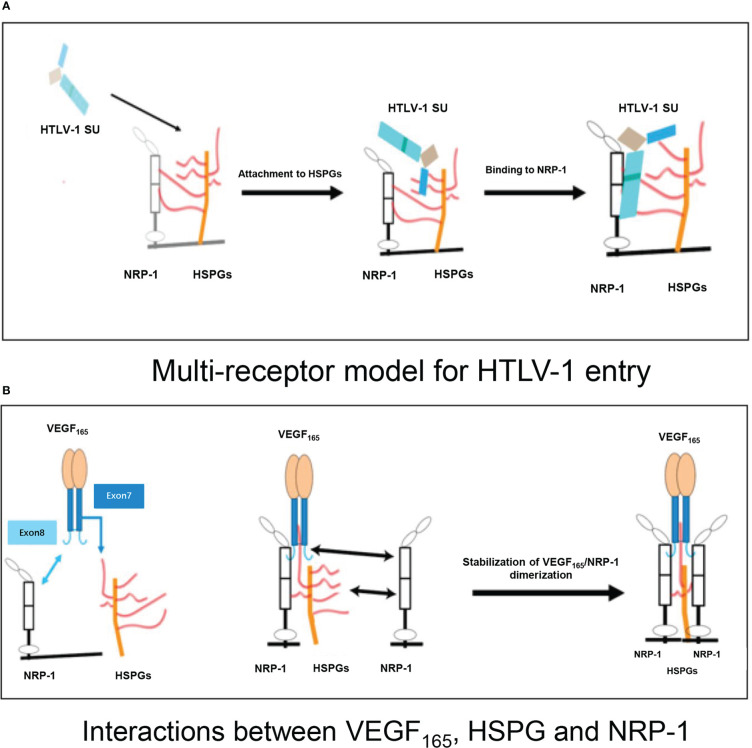
Figure 1.
(A) Multi-receptor model of the initial phase of HTLV-1 entry into target cells. HTLV-1 SU interacts with HSPG, resulting in the initial attachment and concentration of HTLV-1 particles on the cell surface. The interaction of HSPG with SU and NRP-1, and the direct binding of SU to NRP-1 then result in the recruitment of NRP-1, enabling stable binding of SU to the HSPG/NRP-1 complex. (B) Schematic representation of interactions between VEGF165, HSPG, and NRP-1. The sequence encoded by exon 7 of the VEGF165 gene binds to HSPG, and the sequence encoded by exon 8 binds directly to NRP-1. The NRP-1 dimer is then formed, resulting in enhanced stability. HTLV-1: human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1; SU: surface subunit; HSPG: heparan sulfate proteoglycan; NRP-1: neuropilin-1.