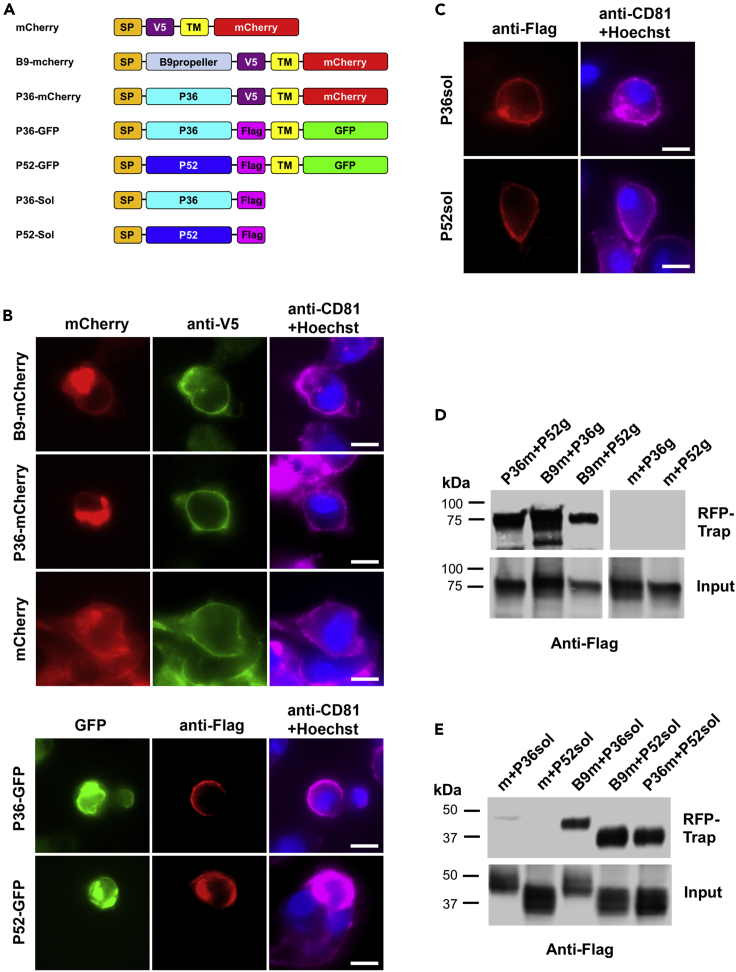
Figure 6.
The propeller domain of B9 interacts with P36 and P52 in a heterologous expression system
(A) Schematic representation of the constructs used for heterologous expression in mammalian cells. SP, signal peptide from the bee venom melittin; TM, transmembrane domain and C-terminal portion of mouse Glycophorin A.
(B) Hepa1-6 cells were examined by fluorescence microscopy 24 h following transfection with mCherry- and GFP-tagged constructs. Cells were fixed without permeabilization and labeled with anti-CD81, anti-V5 or anti-Flag antibodies, and Hoechst 33342. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(C) Hepa1-6 cells transfected with P36-Sol and P52-Sol constructs were fixed without permeabilization and labeled with anti-CD81, anti-Flag antibodies, and Hoechst 33342. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(D and E) Hepa1-6 cells were transiently transfected with constructs encoding mCherry (m), B9-mCherry (B9m), or P36-mCherry (P36m) constructs, together with P36-GFP (P36g), P52-GFP (P52g), P36sol, or P52sol constructs. Following immunoprecipitation of mCherry-tagged proteins, co-immunoprecipitated proteins (RFP-trap) and total extracts (input) were analyzed by western blot using anti-Flag antibodies. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments.