Figure 5.
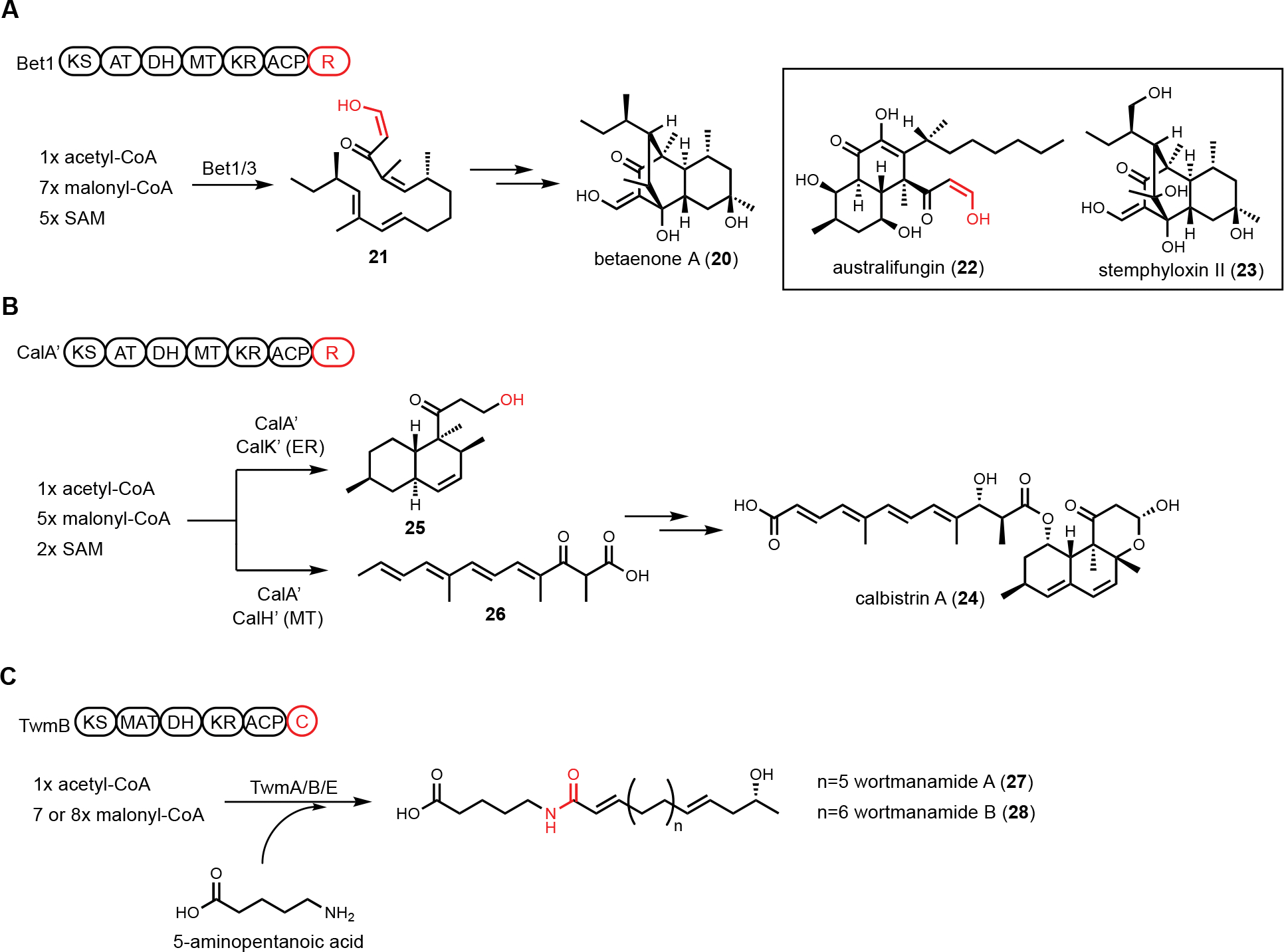
Unusual HRPKS domain arrangement. (A) PKS-R in betaenone biosynthesis. Terminal R domain catalyzes reductive product release. The enol form of aldehyde is highlighted in red. (B) PKS-R in calbistrin A biosynthesis. CalA’ can collaborate with different tailoring enzymes to generate two different polyketide scaffolds. Terminal R domain catalyzes consecutive two-electron reduction to release the decalin product as an alcohol, which is highlighted in red. (C) PKS-C in wortmanamide biosynthesis. The C domain fused with PKS is able to catalyze long chain N-acyl amide formation.
