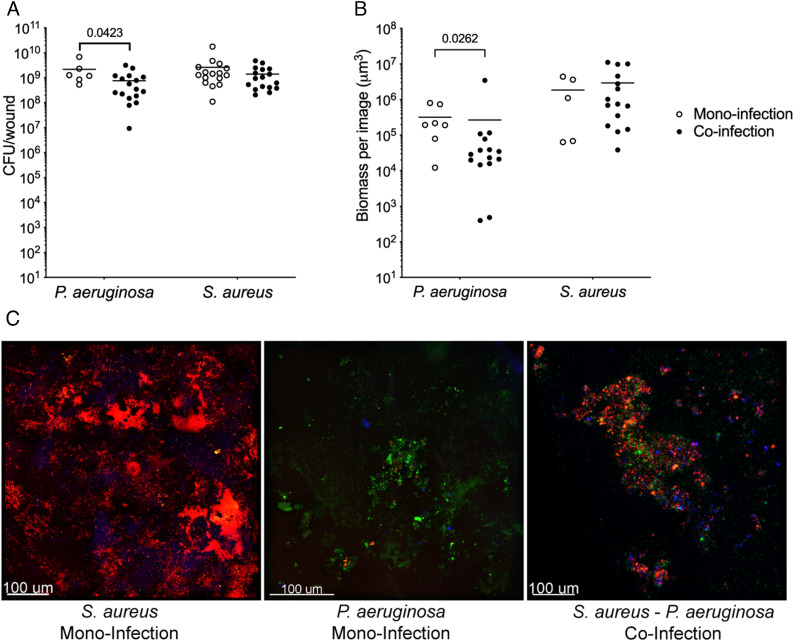
Fig. 1.
S. aureus and P. aeruginosa coexist in a murine surgical wound model. (A) Bacterial burdens in mono- (open circles) and co-infected (closed circles) murine chronic wounds 4 d post infection. Number of animals used was as follows: P. aeruginosa monoinfection n = 6, S. aureus monoinfection n = 16, S. aureus/P. aeruginosa coinfection n = 17. (B) Bacterial biomass measured by confocal microscopy of murine wounds infected with S. aureus or P. aeruginosa alone (monoinfection, open circles) or together (coinfection, closed circles). P-values shown were determined using a Mann–Whitney test. (C) Confocal microscopy of murine wounds infected with S. aureus (red, first panel) or P. aeruginosa in monoinfection (green, second panel) or in coinfection (third panel) at 4 d postinfection. Host cells (blue) were stained with NucBlue in the mounting medium.