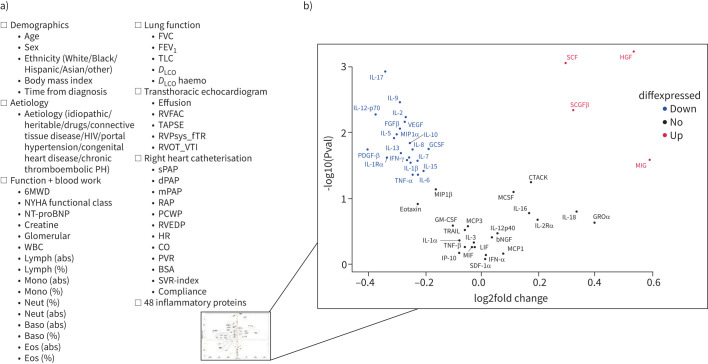
FIGURE 1.
a) An outline of all biomarkers considered; b) volcano plot showing all circulating proteins considered with fold change (concentration in high-risk patients/concentration in low-risk patients) in high 4-year risk, relative to low 4-year risk. Proteins in red and blue represent those that were statistically higher or lower (p<0.05), respectively, and with a |foldchange| >1. PH: pulmonary hypertension; 6MWD: 6-min walk distance; NYHA: New York Heart Association; NT-proBNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; WBC: white blood cells; lymph: lymphocytes; abs: absolute; mono: monocytes; neut: neutrophils; baso: basophils; eos: eosinophils; FVC: forced vital capacity; FEV1; forced expiratory volume in 1 s; TLC: total lung capacity; DLCO: diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; DLCO haemo: DLCO adjusted for haemoglobin during pulmonary function testing; RVFAC: residual volume fractional area change at transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE); TAPSE: tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion; RVPsys_fTR: right ventricle (RV) systolic pressure computed from tricuspid regurgitation; RVOT_VTI: RV outflow tract velocity time integral at TTE; sPAP: systolic pulmonary arterial pressure; dPAP: diastolic pulmonary arterial pressure; mPAP: mean pulmonary arterial pressure; RAP: right atrial pressure; PCWP: pulmonary capillary wedge pressure; RVEDP: RV end-diastolic pressure; HR: heart rate; CO: cardiac output; PVR: pulmonary vascular resistance; BSA: body surface area; SVR: systemic vascular resistance.