Fig. 1.
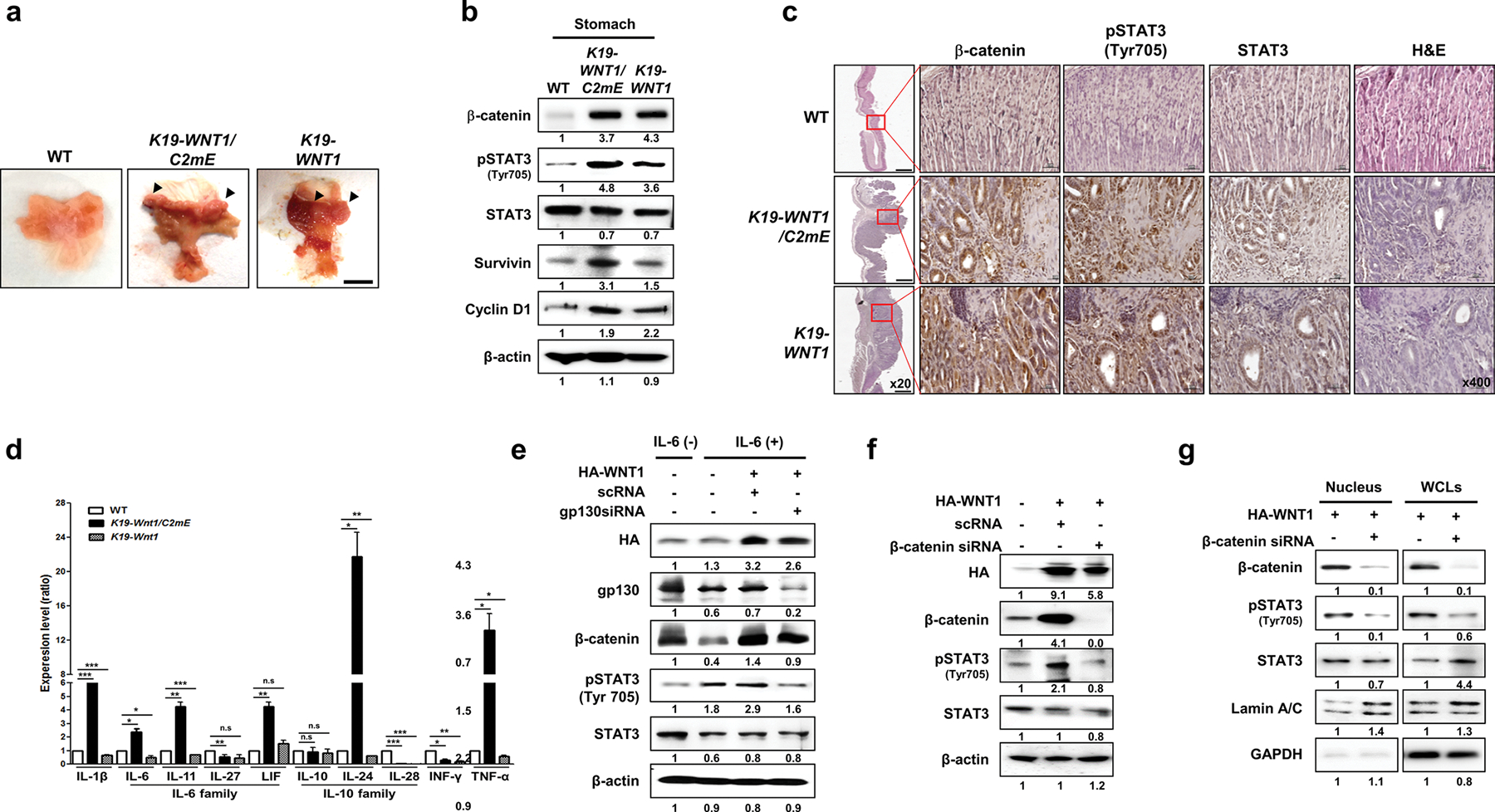
Overexpression of WNT1 induces the phosphorylation and nuclear accumulation of STAT3 in a cytokine receptor-independent but β-catenin-dependent manner. a Representative whole stomachs from wild-type (WT) mice and K19-WNT1/C2mE and K19-WNT1 transgenic mice at 45 weeks. The arrows indicate regions of hyperplasia. Scale bar, 5 mm. b Levels of the indicated proteins in whole stomach tissues from the three mouse lines (indicated at top) as detected by western blotting of extracts. c Immunohistochemical analysis of β-catenin, STAT3, and pSTAT3(Tyr705) in stomach tissues from WT mice and K19-WNT1/C2mE and K19-WNT1 transgenic mice. Scale bars, 500 μm under low magnification (20×) and 20 μm under high magnification (400×). d Gene expression levels of various cytokines (indicated at bottom) as detected by quantitative RT-PCR of whole stomach tissues from the three mouse types. Levels are given as the mean ± SEM ratio to that of WT mice (n = 3). Significant differences are indicated by asterisks (n.s., *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001, and ***p = 0.0001). p values were calculated using Student’s t test. e Western blotting of the indicated proteins in IL-6 untreated non-transfected AGS cells (lane 1) and in IL-6-treated cells with or without HA-WNT transfection and gp130 silencing by siRNA (indicated at top). The relative pSTAT3 level is shown below the blots. f Detection of the indicated proteins in AGS cells with or without transfection with HA-WNT1 and β-catenin siRNA. g Detection of the indicated proteins in nuclear and whole cell lysates (WCLs) of AGS cells with or without transfection with HA-WNT1 and β-catenin siRNA. Lamin A/C and GAPDH were used as nuclear and cytosolic markers, respectively
