Fig. 1.
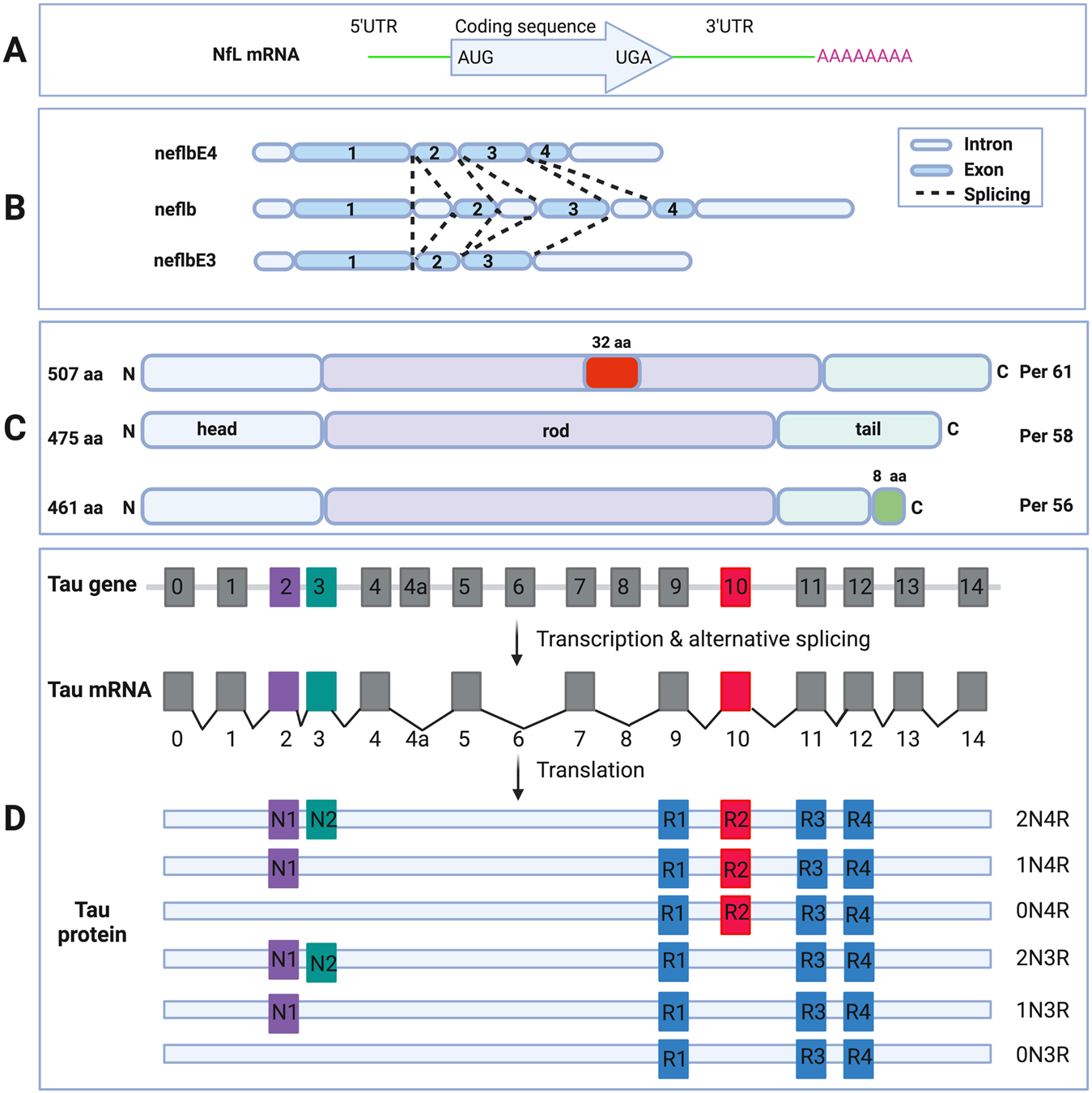
Schematic diagram of NfL mRNA (A). 5’UTR, protein coding region, 3’UTR and the poly-A tail are shown (upper box). Schematic diagram of the neflb isoforms, generated by alternative splicing of the same mRNA in zebrafish (B). neflb is expressed at all embryonic and larval stages in zebrafish, which a splicing shift from neflbE3 to neflbE4 occurring during CNS development. Schematic diagram of the PRPH isoforms, generated by alternative splicing of the same mRNA (C). Per 58 is the major constitutive form; Per 61 results from the insertion of 32 aa in the rod domain; Per 56 results from the replacing the C-terminal 21 aa with a different 8 aa sequence. Schematic diagram of MAPT gene, mRNA and splice isoforms of tau in the human brain (D). Human MAPT gene contains 16 exons. E1, E4, E5, E7, E9, E11, E12 and E13 are constitutive, whereas others are subject to alternative splicing. E0 and E1 encode the 5’UTR, whereas E14 is part of the 3’UTR. E4a, E6 and E8 are transcribed only in peripheral tissues. The alternative splicing of E2, E3 and E10 give rise to 6 different mRNAs, which are translated to 6 isoforms. These isoforms differ by the presence of 1 or 2 N-terminal inserts encoded by E2 (purple box) and E3 (green box), in combination with the presence of either 3 or 4 repeat regions coded by E9 (blue box), E10 (red box), E11 (blue box) and E12 (blue box) in the C-terminus.
