Figure 1. Overall architecture of FoxP3.
See also Figures S1 & S2.
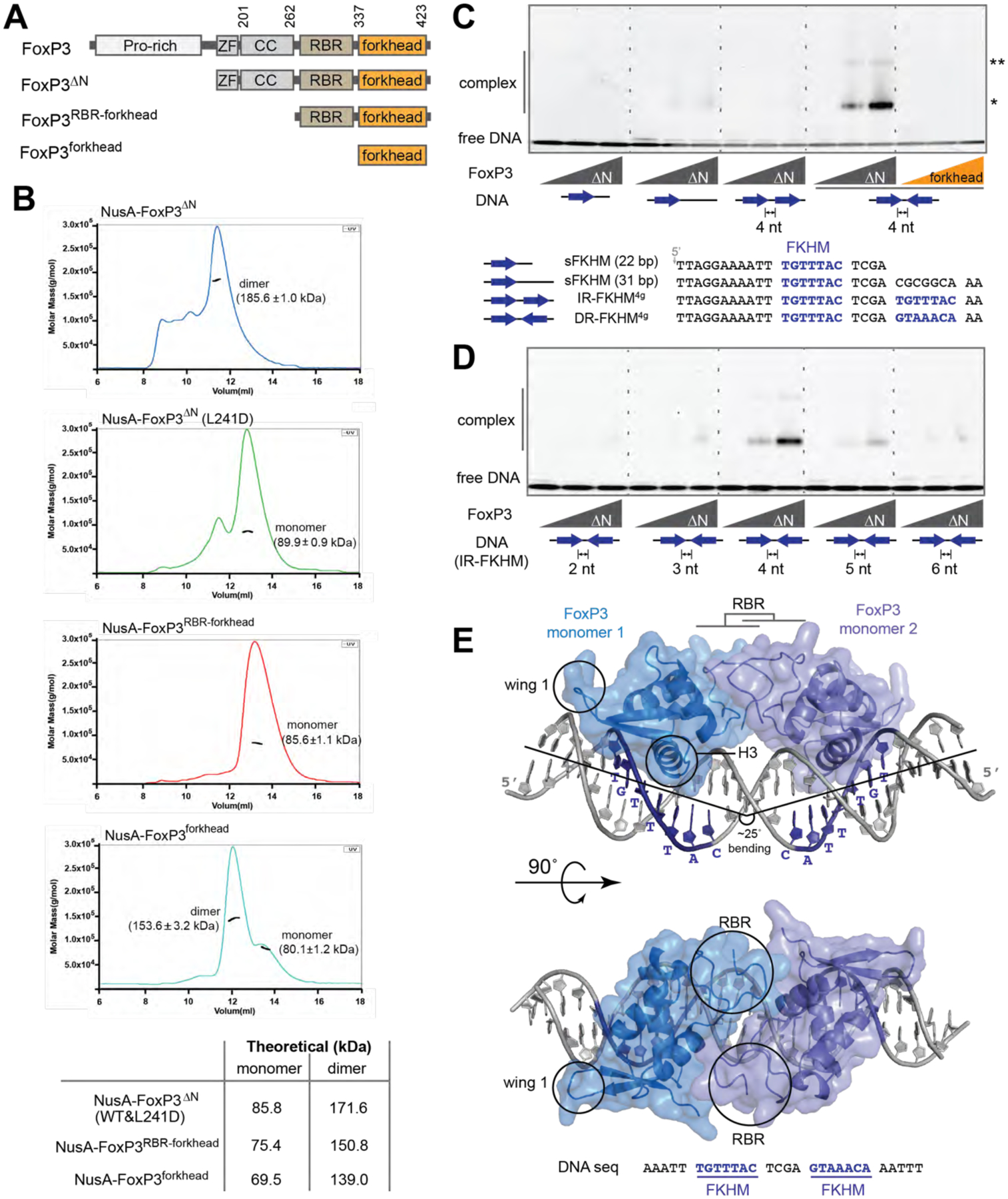
A. Domain architecture of FoxP3ΔN, FoxP3RBR-forkhead and FoxP3forkhead. (ZF: zinc finger; CC: coiled coil; RBR: Runx1-binding region).
B. SEC-MALS of various truncation variants of FoxP3. Experimentally determined mass values are shown in parenthesis on the graphs. Theoretical values are shown in the table below. The NusA tag was fused for all constructs to increase the accuracy of mass estimation. L241D disrupts CC dimerization.
C. EMSA of FoxP3ΔN or FoxP3forkhead (0, 0.4 and 0.8 μM) using four DNA oligos (0.2 μM) with different FKHM arrangements. Sybr Gold stain was used to visualize DNA. While FoxP3ΔN binds DNA predominantly as a dimer (*), a small population of higher-order oligomer (**) was also seen.
D. EMSA of FoxP3ΔN (0, 0.4 and 0.8 μM) with DNA containing IR-FKHM (0.2 μM) with varying gap sizes.
E. Crystal structure of Foxp3ΔN in complex with IR-FKHM4g DNA. Two non-swap FoxP3 monomers form a head-to-head dimer through the RBR loop. ZF and CC were present in the crystal (See Figure S2E), but were not resolved. The helix 3 (H3) and wing 1 that are characteristics of the canonical forkhead structure are indicated with circles.
Data in (B-D) are representative of at least three independent experiments.
