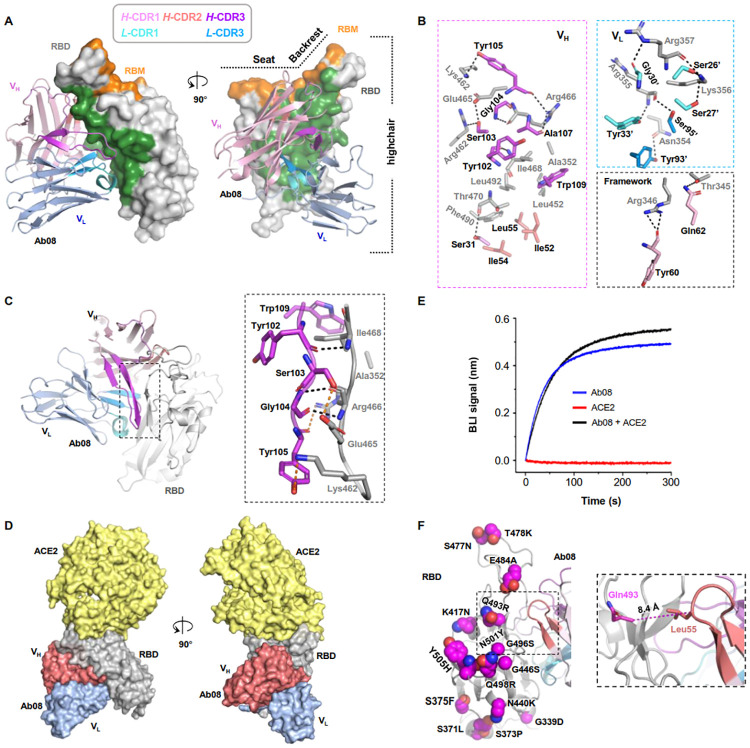
Fig 3. Structural characterization informs mechanism for the relatively broad activity of Ab08.
(A) The overall structure of the Ab08 (scFv) (cartoon) in complex with the high-chair-shaped RBD (grey surface). The Ab08 epitope is colored green. RBD-interacting CDRs are color-coded as indicated. (B) Interactions between RBD (grey) and Ab08. CDR residues are color-coded as in A. Ab08 residues are labeled black and RBD residues are labeled grey. A prime symbol indicates residues from the light chain. Dash lines indicate distances within 3.6 Å. (C) The β-sheet interaction between Ab08 and RBD. Backbone- and side-chain-mediated H-bonds are indicated by black and orange dash lines, respectively. (D, E) Ab08 is compatible with ACE2-binding. (D) Structural alignment of ACE2-RBD (PDB ID 6M0J) and Ab08-RBD (this work) reveals no clashes between ACE2 (yellow) and Ab08 (red and blue). (E) Ab08 and ACE2 simultaneously bind RBD. A sensor immobilized with RBD was soaked in 100 nM of ACE2 before being further soaked in ACE2-containing buffer with (black) or without (red) 100 nM of Ab08 for BLI signal recording. As a control, the Ab08-RBD interaction was monitored in the absence of ACE2 (blue). (F) The distribution of the Omicron mutations. Of the 15 mutations, only one (Q493R) occurs at the epitope but the relative long Cα distance (8.4 Å) between RBD Gln493 and Ab08 Leu55 suggests neglectable impact of Q493R on Ab08-RBD interactions.