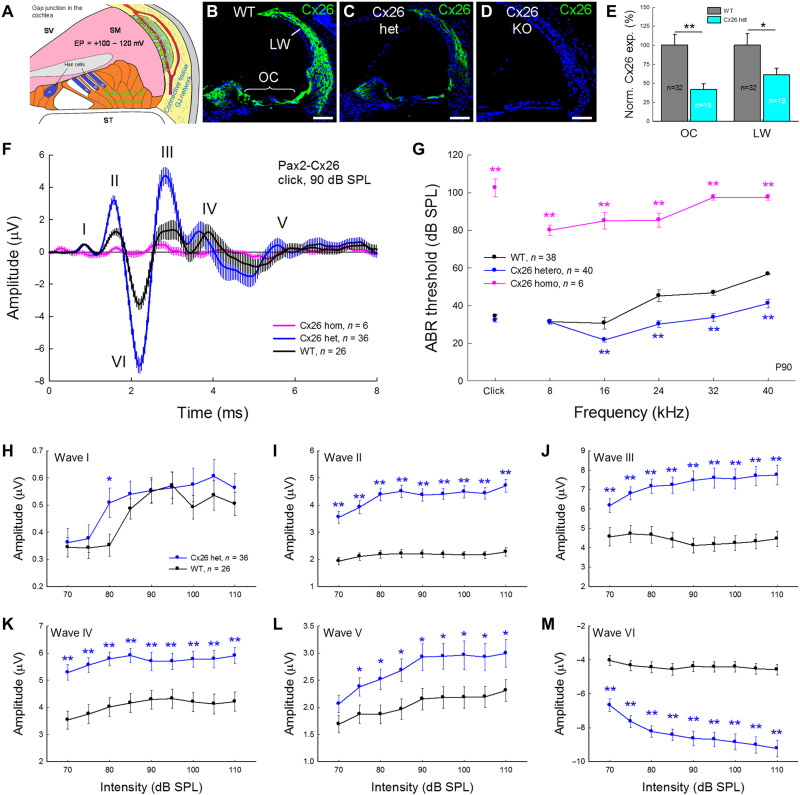
Fig. 1. Increase of hearing sensitivity in Pax2-Cx26+/− hetero-deletion mice.
(A) Diagram of GJ network in the cochlea. Hair cells have neither GJ nor connexin expression. SV, scala vestibuli; SM, scala media; ST, scala tympani. (B to D) Immunofluorescent staining for Cx26 (green) in the cochlea. Cx26 has labeling in Cx26+/− mice but the intensity of labeling is weaker than that in WT mice (C). No labeling is visible in Cx26−/− cKO mice (D). OC, the organ of Corti; LW, lateral wall; WT, wild type; KO, knockout. Scale bars, 50 μm. (E) Quantitative analysis of Cx26 labeling at the OC and LW in Pax2-Cx26+/− mice. The intensity of labeling was normalized to the average value in WT mice. The expression of Cx26 in Cx26+/− mice was reduced by ~50%. (F) Averaged ABR traces recorded from WT, Cx26+/−, and Cx26−/− mice. The ABR traces were evoked by 90 dB of sound pressure level (SPL) click stimulations and averaged. Bars represent SEM. Mice were 90 days old. (G) ABR thresholds in Cx26+/− mice were significantly reduced in comparison with those in WT mice. Pink line and symbols represent ABR thresholds recorded from Pax2-Cx26−/− cKO mice, which appeared as severe hearing loss. (H to M) Quantitative measurement of ABR peaks in Pax2-Cx26+/− mice. ABRs were evoked by click stimuli. The amplitudes of waves II to VI in Cx26+/− mice were significantly increased in comparison with WT mice. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, two-tailed t test.