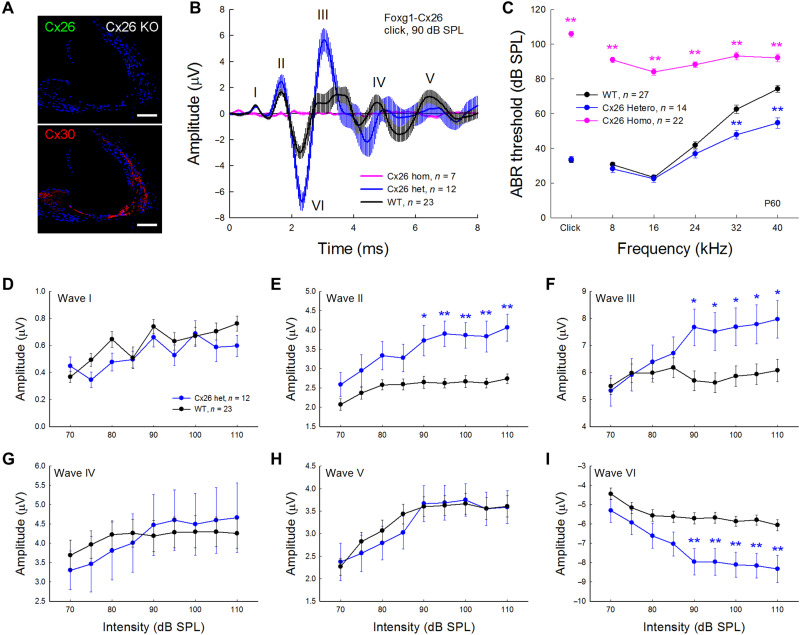
Fig. 2. Increase of hearing sensitivity in Foxg1- Cx26+/− hetero-deletion mice.
(A) Cx26 deletion in the cochlea in Foxg1-Cx26−/− cKO mice. Immunofluorescence staining shows negative staining for Cx26 in the Foxg1-Cx26−/− mouse cochlea. Cx30 staining in the cochlea of Cx26−/− mice appears normal. Scale bars, 50 μm. (B) Averaged traces of ABR recorded from WT, Foxg1-Cx26+/−, and Foxg1-Cx26−/− mice. The traces were evoked by 90 dB SPL of click stimuli and averaged from different mice. Bars represent SEM. Mice were 60 days old. ABR waves in Foxg1-Cx26+/− mice are larger than those in WT mice. The pink line near the base line represents the evoked ABR trace in Foxg1-Cx26−/− cKO mice. (C) ABR thresholds in Foxg1-Cx26+/− mice were significantly reduced in comparison with those in WT mice. WT littermates served as control. Pink lines and symbols represent ABR thresholds recorded from Foxg1-Cx26−/− cKO mice, which appeared as severe hearing loss or deafness. **P < 0.01, two-tailed t test versus WT mice. (D to I) Quantitative measurement of ABR waves in Foxg1-Cx26+/− mice. ABRs were evoked by click stimuli, and the peaks of waves I to VI were measured and averaged. The amplitudes of waves II, III, and VI at high intensities in Cx26+/− mice were significantly increased in comparison with those in WT mice. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, two-tailed t test.