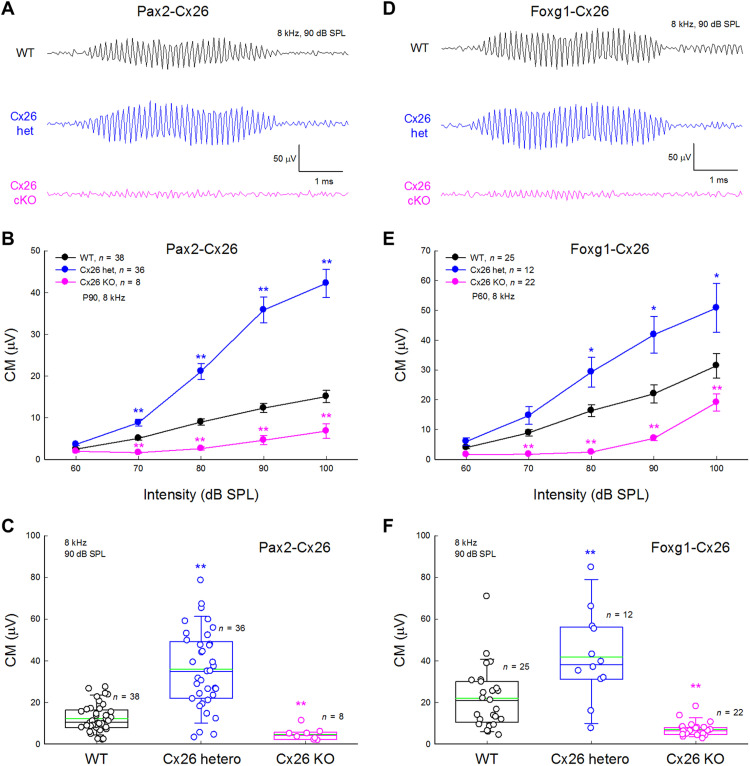
Fig. 3. Increase of CM in Pax2-Cx26+/− mice and Foxg1-Cx26+/− mice.
(A) CM traces recorded from WT, Pax2-Cx26+/−, and Pax2-Cx26−/− mice. CM was evoked by 90 dB SPL, 8 kHz of tone bursts. (B) CM in Pax2-Cx26+/− mice was significantly increased in comparison with that in WT mice, whereas CM in Pax2-Cx26−/− cKO mice was significantly reduced. Mice were 3 months old. **P < 0.01, two-tailed t test versus WT. (C) CM in WT, Pax2-Cx26+/−, and Pax2-Cx26−/− mice at stimulation of 90 dB SPL, 8 kHz of tone bursts. Green lines in the boxes represent the mean levels. In comparison with WT mice, CMs in Pax2-Cx26+/− were significantly increased and CMs in Pax2-Cx26−/− mice were significantly reduced. **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni correction. (D to F) CM recorded from WT, Foxg1-Cx26+/−, and Foxg1-Cx26−/− mice by 90 dB SPL, 8 kHz of tone bursts. Mice were 2 months old. In comparison with that in WT mice, CM in Foxg1-Cx26+/− mice was significantly increased while CM in Foxg1-Cx26−/− cKO mice was significantly decreased. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01, two-tailed t test versus WT in (E) and one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni correction in (F).