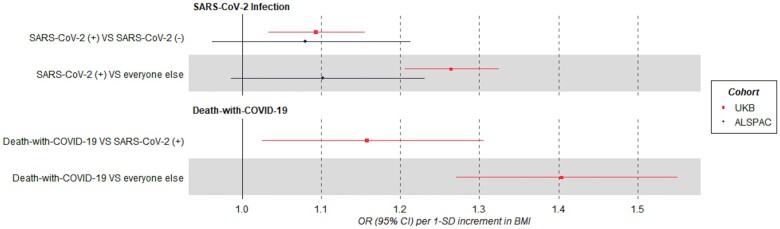
Figure 3.
Forest plots of the association between BMI and COVID-19-related outcomes. In the ALSPAC cohort of young adults; SARS-CoV-2(+) vs SARS-CoV-2(−) N=1915, SARS-CoV-2(+) vs ‘everyone else’ N=2983. In UKB; SARS-CoV-2(+) vs SARS-CoV-2(−) N=4662, SARS-CoV-2(+) vs ‘everyone else’ N=409 487. Death-with-COVID-19 vs SARS-CoV-2(+) not resulting in death-with-COVID-19 N=1375, death-with-COVID-19 vs ‘everyone else’ N=409 487. Models were adjusted for age, sex, smoking, education and proxies of socio-economic position. ‘Everyone else’ control group includes those tested and SARS-CoV-2(−) and those not tested. BMI, body mass index; ALSPAC, Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children; UKB, UK Biobank; OR, odds ratio.