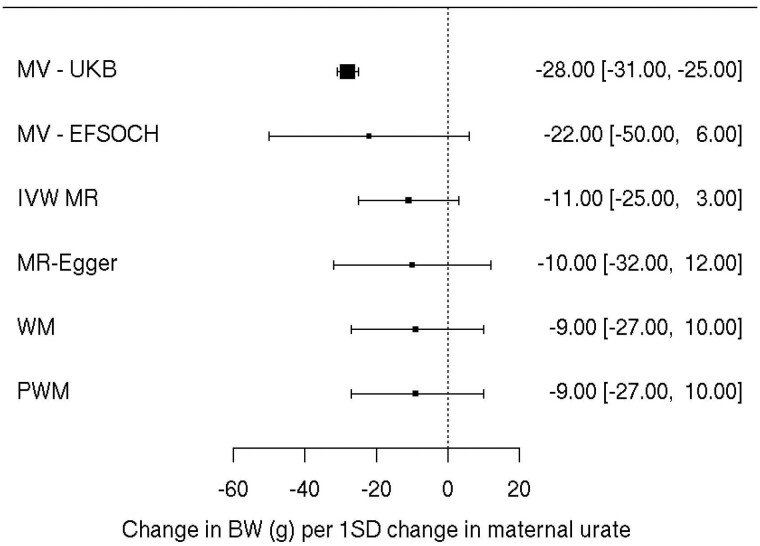
Figure 2.
Forest plot of the effect of maternal serum urate on offspring birthweight: observationally using participants in UK Biobank (n = 133 187), observationally using participants in the Exeter Family Study of Childhood Health (n = 872) and using univariate Mendelian randomization (inverse-variance weighted method) with additional sensitivity methods. Each estimate is the change in birthweight in grams per 1-SD change in urate level (95% CI). The MR–Egger analysis indicated no sign of horizontal pleiotropy with an intercept near zero [–0.07 (95% CI: –0.22, 0.08)]. The sizes of the black boxes are a reflection of the sample size for each analysis—the larger the box, the greater the sample size, with the bracketing segments representing the 95% CIs. MV, multivariable linear regression; UKB, UK Biobank; EFSOCH, Exeter Family Study of Childhood Health; IVW, inverse-variance weighted; MR, Mendelian randomization; WM, weighted median; PWM, penalized weighted median; BW, birthweight