Figure 1.
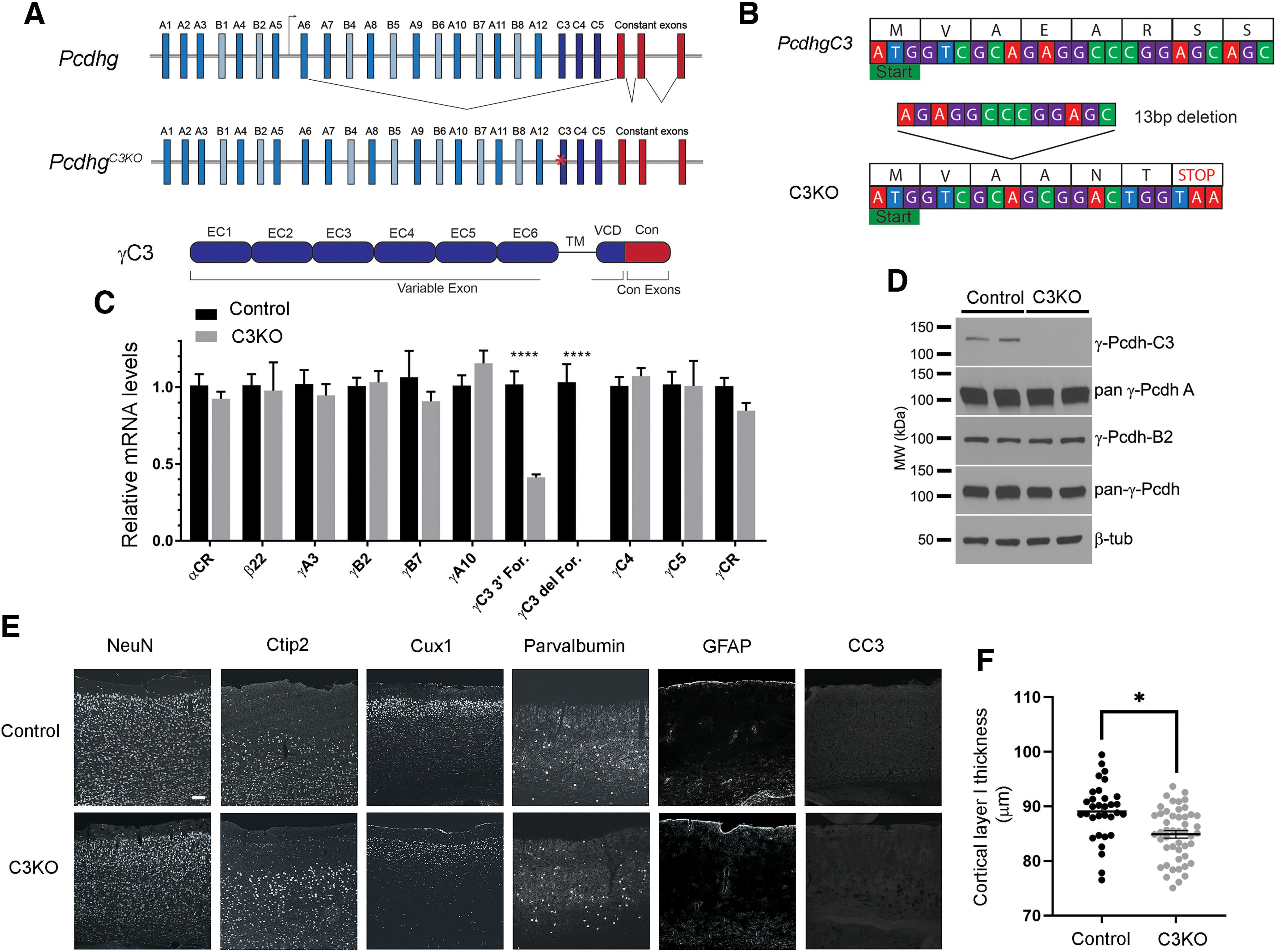
Generation of the C3KO mouse. A, Schematic representation of: the mouse Pcdhg locus, comprising 22 variable exons (γA-types: blue, γB-types: cyan, and γC-types: dark blue) which are spliced to three constant exons (red); the PcdhgC3KO locus, with frameshift deletion in the C3 variable exon indicated by a red asterisk; and the γC3 protein domain structure, with six extracellular cadherin repeats, a transmembrane domain, and a short variable cytoplasmic domain (all encoded by the variable exon) followed by a shared cytoplasmic domain (encoded by the three constant exons). B, Start of the mouse Pcdhgc3 gene with protein translation. A 13-bp deletion in the C3KO allele results in a frameshift, leading to an early stop codon. C, Quantitative PCR performed on cortical cDNA for multiple cPcdh genes shows specific loss of the γC3 isoform (no signal using a forward primer spanning the deletion; reduced transcript levels using a forward primer at the 3′ end of the variable exon), while other cPcdh and overall Pcdhg expression remain unaltered. Data are presented as relative mRNA as compared with GAPDH. ±SEM from six individual animals. A two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test was performed to assess statistical significance. ****p < 0.0001. D, Western blottings from cortical lysates show no γC3 expression in the C3KO, while expression of other γ-Pcdhs remain largely unaltered. E, F, Cryosections of adult C3KO, and control S1 cortices were stained with multiple layer-specific and cell type-specific markers, which indicate grossly normal cell types and morphology in C3KO mice, save for a somewhat thinner Layer I, suggesting a loss of apical dendritic tufts as was seen for complete Pcdhg cluster KO mice (Garrett et al., 2012). Scale bar: 100 µm.
