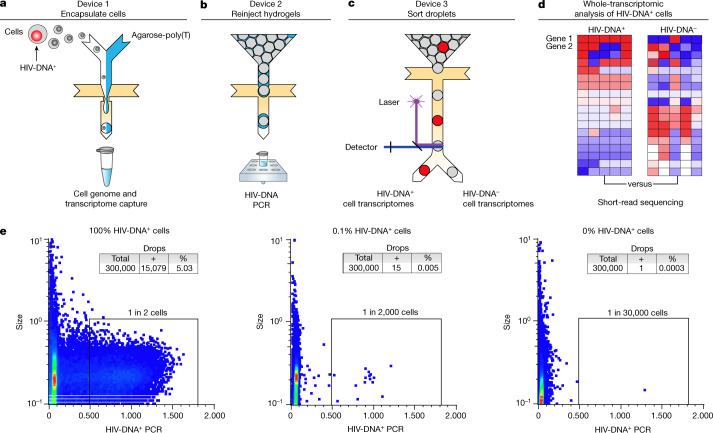
Fig. 1. Whole-transcriptomic analysis of HIV-DNA+ cells using FIND-seq.
a–d, Overview of the workflow, including three sequential microfluidic devices separated by handling steps. a, On the first device, single cells are encapsulated at a limiting dilution in a water-in-oil emulsion with lysis buffer and molten agarose-poly(T). The agarose is then cooled to form a hydrogel bead that retains genomic DNA and polyadenylated RNA. After oil removal, whole-transcriptome cDNA is covalently linked to the hydrogel by reverse transcription for subsequent whole-transcriptome amplification (WTA) using PCR (see Extended Data Fig. 1a–e). b,c, Hydrogel beads re-encapsulated on the second device are analysed using droplet PCR for HIV gag (b) and then sorted on the third device (c). d, The processing steps performed after droplet sorting include WTA, library preparation and sequencing, and bioinformatic comparison of HIV-DNA+ cells and HIV-DNA− cells. e, Droplet cytometry plots demonstrating the analysis of pure HIV-DNA+ J-Lat T cells (left), pure HIV-DNA− Jurkat T cells (right), and a mixture of 0.1% J-Lat and 99.9% Jurkat cells (middle). Cells were encapsulated at 1 cell per 10 droplets.