Figure 1:
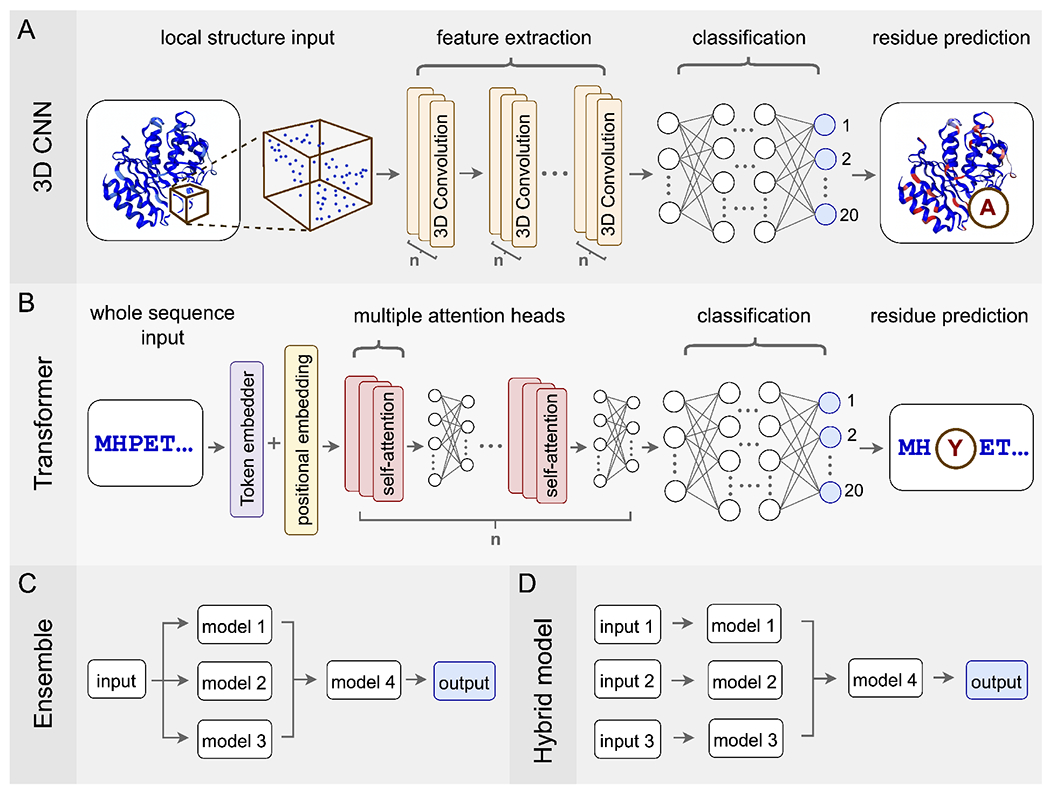
Commonly used network architectures for predicting mutations in protein sequences or structures. (A) 3D Convolutional Neural Networks (3D CNNs) take all the atoms in a subset of 3D space as input, use convolutional layers to extract features, and then use a traditional multilayer perceptron for classification. (B) Transformer models take protein sequences as input, which they process via embedding combined with the attention mechanism. The final classification occurs with a multilayer perceptron, just like for 3D CNNs. (C) Ensemble models process the same set of input data via multiple independent models, whose predictions are then combined into a final output. (D) Hybrid models are architecturally similar to ensemble models but now each of the independent models can have different input data, such as sequence data, structural data, phenotypic measurements, etc.
