Figure 1. Types of non-coding RNAs and schematic of Circular (circRNAs) and enhancer (eRNAs) RNAs.
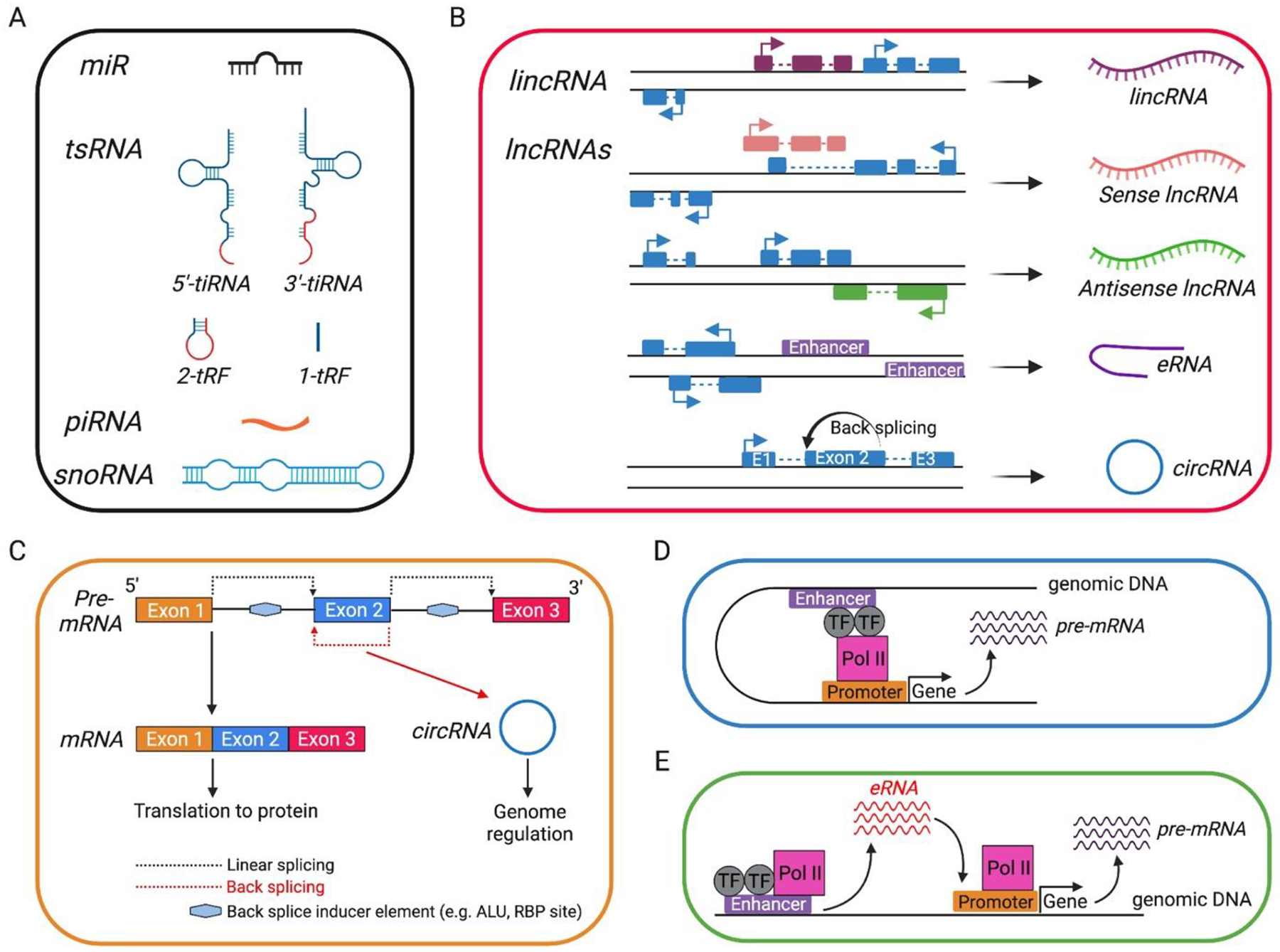
A, Small ncRNAs. B, Long ncRNAs. In B, coding exons are denoted as blue boxes. C, pre-mRNA (above) can be spliced in a linear fashion to generate mRNA (below left) or undergo back-splicing to generate circRNA (below right). D, conventional enhancers participate in DNA looping bringing transcription factors (TF) and polymerase II (Pol II) together with gene promoters to enhance gene transcription. E, some enhancers are themselves transcribed to non-coding RNAs (called eRNAs) that participate in loop formation to enhance gene transcription. For simplicity, loop formation has not been depicted in the cartoon in E. miR, micro-RNA; tsRNA, tRNA-derived small RNA (5’-tiRNA/3’-tiRNA, stress induced tRNA-derived RNAs from 5’ or 3’ ends of tRNA; 2-tRF, anti-codon loop cleaved by unknown ribonuclease; 1-tRF, generated by RNase Z in the 3’ trailer of tRNA); piRNA, piwi-interacting RNA, snoRNA, small nucleolar RNAs; lncRNA, linear long non-coding RNA; lincRNA, long intergenic non-coding RNA (lncRNAs that do not overlap with protein-coding genes); eRNA, enhancer RNA; circRNA, circular RNA.
