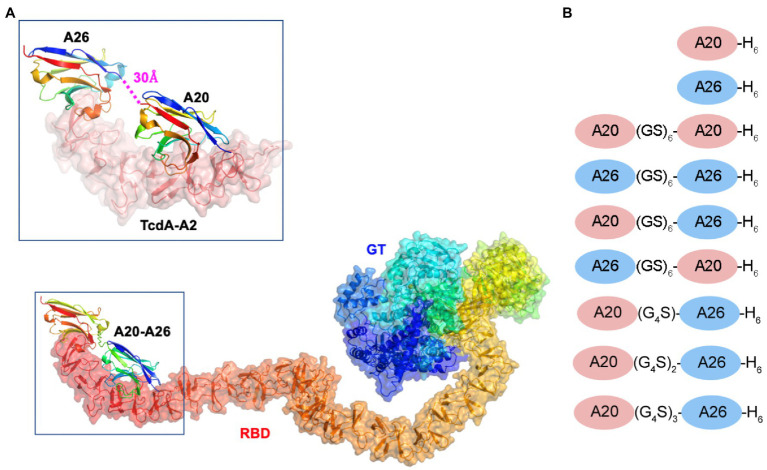
Figure 1.
Model of the A20-A26 fusion protein bound to the CROPs domain of Clostridioides difficile TcdA. (A) The structure of full-length C. difficile TcdA was generated by superimposing the crystal structure of the N-terminal 1832 amino acid residues of TcdA (4R04) (Chumbler et al., 2016) onto the crystal structure of TcdB (6OQ5) (Chen et al., 2019). To model the CROP domain missing from the TcdA structure, we made the assumption that the orientation of the CROP domain relative to the N-terminal domains is similar in the two toxins. By superimposing the N-terminal short repeat of a model of the TcdA CROP domain (Ho et al., 2005; Pruitt et al., 2010; Pruitt and Lacy, 2012) onto the N-terminal short repeat in the CROP domain of TcdB (6OQ5), a model of full-length TcdA was generated. The resulting model shows similar features to the low resolution cryo-EM envelopes of full-length TcdA (Pruitt et al., 2010; Pruitt and Lacy, 2012). The structure of the complex formed between A20-A26 and TcdA was generated by modeling the structure of a (GS)6 linker in an extended antiparallel β-strand conformation using PyMOL and positioning this linker between the C-terminus of the A20 VHH and the N-terminus of the A26 VHH observed in the crystal structure of the complex formed between A20, A26 and the TcdA-A2 fragment (4NC1) (Murase et al., 2014). TcdA is shown in cartoon ribbon and semi-transparent surface representations. A20, A26 and the A20-A26 VHH domains are drawn in cartoon representation. Each polypeptide chain is colored according to the colors of the rainbow, starting from blue at the N-terminus to red at the C-terminus. RBD, receptor binding domain; GT, glucosyl transferase. (B) Schematic representation of the VHH constructs generated in this work.