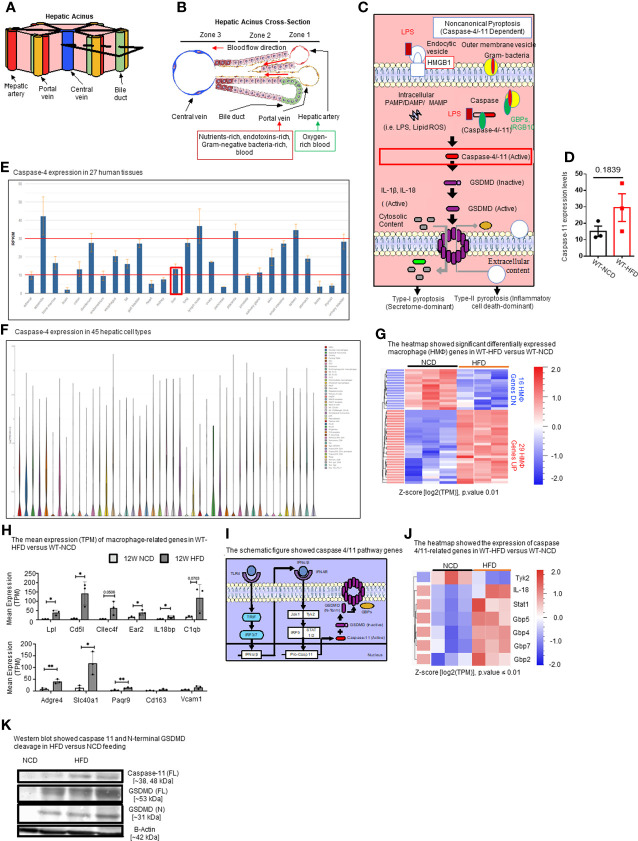
Figure 2.
HFD upregulates the expressions of proinflammatory, NASH-related hepatic macrophage markers, GBPs, caspase-11, and increases N-terminal GSDMD cleavage. (A, B) The structure of hepatic acinus suggests that the liver is the first organ exposed to endotoxins-rich and Gram bacteria-rich blood in the body. Liver parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells are organized into structures called “acinus”. Hepatic acini form hexagonal structures with a central vein and portal triad at the vertices. The hepatic acinus can be histologically divided into three zones. Zone 1 represents the portal triad which includes a hepatic artery, a portal vein, and a bile duct. Zone 2 represents the parenchymal area, structurally consisting primarily of hepatocytes with a central vasculature composed of liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs). Mature immune cells including B cells, T cells, innate-like lymphoid cells (ILCs), natural killer cells (NK cells), and tissue-resident macrophages (Kupffer cells) reside in hepatic acinus zone 1 and 2. Zone 3 represents the central vein, the innermost hepatocytes, and infiltrating immune cells. The portal vein contains nutrient-rich, endotoxins-rich, and gram bacteria-rich blood. (C) Noncanonical pyroptosis is caspase-4 (human), caspase-11 (mouse) dependent. Guanylate binding proteins (GBPs) promote the outer membrane vesicles from gram-bacteria to activate caspase-11. Intracellular sources of inflammation (including LPS and oxidized phospholipids) directly bind to caspase-4/-11. Caspase-4/-11 cleaves gasdermin-D to initiate noncanonical pyroptosis. (D) The expressions of caspase-11 in the liver were in an upregulation trend in high-fat diet-fed wild-type mice. The microarray data were achieved from the NIH-NCBI-Geo-Profiles database (GDS4811). (E) Caspase-4 expression in 27 human tissues. The expression of caspase-4 in the liver is at a medium level among all 27 human tissues. Caspase-4 RNA-Seq data were analyzed from the NIH-NCBI-Gene database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/837). (F) Caspase-4 expression in 45 hepatic cell types. Caspase-4 is expressed in all 40 immune cell types, the single-cell RNA-Seq data were analyzed from the MIT Broad Institute Single Cell RNA-Seq (scRNA-Seq) Porter database (https://singlecell.broadinstitute.org/single_cell/study/SCP1845/cross-tissue-immune-cell-analysis-reveals-tissue-specific-features-in-humans?genes=casp4%26tab=distribution#study-visualize). Among 45 immune cell types identified in scRNA-Seq, 19 immune cell types are significantly enriched in the human liver including dendritic cell 1 (DC1), DC2, classical monocytes, non-classical monocytes, erythrophagocytic macrophages, mononuclear phagocytes (MNP)/B doublets, age-associated B cells (ABCs), plasma cells, Plasmablasts, MNP/B doublets, T/B doublets, mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT), T_CD4/CD8, T effector memory (Tem)/effector memory re-expressing CD45RA (emra)_CD8, T resident memory cell/effector memory cell (Trm/em)_CD8, gamma-delta T cell (Tgd)_CRTAM+, Cycling T cell & natural killer cell (NK), NK_CD16+, and NK-CD56bright_CD16-. (G) 12-week HFD promotes expression of HMΦ activation mediators in the WT liver. 8-10 weeks old male WT mice were fed with HFD for 12 weeks. Heatmap of significant, differentially regulated macrophage (HMΦ) genes. (H) Bulk RNA-seq expression (mean transcripts per kilobase million, TPM) of macrophage mediators. (I) Schematic representing caspase-4/11 pathway genes. (J) Bulk RNA-seq expression (mean TPM) of noncanonical pyroptosis-associated mediators. (K) Western blot analysis showed that HFD feeding increased caspase-11 and N-terminal GSDMD cleavage. Statistical Analysis: Bulk RNAseq analysis was performed using Qlucore Omics Explorer. Heatmap was generated using significantly differentially regulated genes (p.adj < 0.01). Differential gene expression presented as Z-score calculated from log2 transformed TPM. *P < 0.05, **p < 0.01.