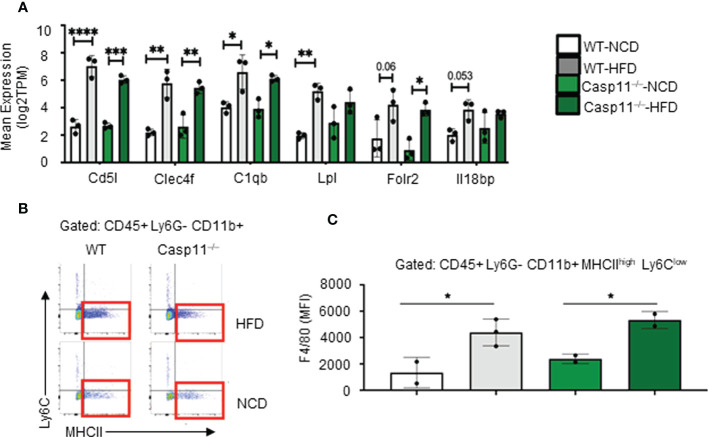
Figure 3.
High-fat diet (HFD)-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) drives the increase of NASH-related F4/80+ hepatic macrophages (HMΦs) in WT mice, which are caspase-11 activation-independent. 8-10 weeks old male WT and Casp11–/– mice were fed HFD for 12 weeks. (A) Bulk RNA-seq expression (TPM) of NASH-associated activated HMΦ genes. (B) Representative flow cytometry gating of HMΦ. Gated on CD45+ > CD11b+ Ly6G- > Ly6Clow MHCIIhigh. (C) F4/80+ mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) for HMΦ populations. Statistical Analysis: Bulk RNAseq analysis was performed using Qlucore Omics Explorer. PCA generated using significantly differentially regulated genes (p.adj < 0.01). Included genes were significant (p < 0.05) in multi-variant analysis (Two-Way ANOVA). Marked significance (*) determined by One-Way ANOVA. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001 ****p < 0.0001. Flow cytometry data was analyzed with FlowJo, and statistical analysis was performed using Prism. One-Way ANOVA.