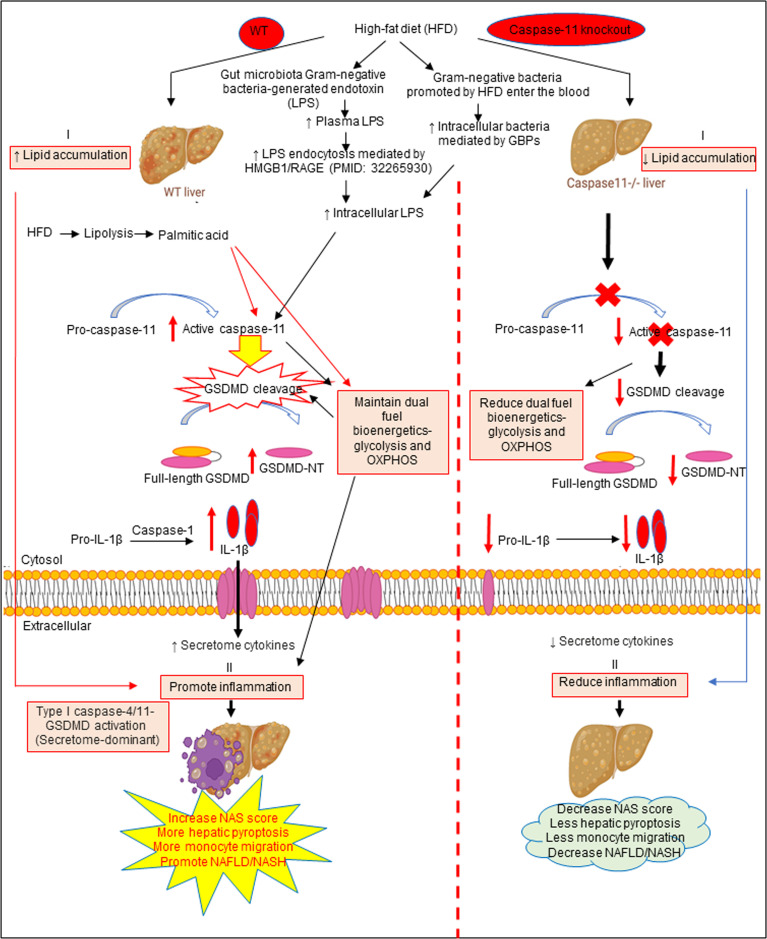
Figure 6.
The working model showed that HFD increased hepatic lipid accumulation (steatosis). HFD promotes increased gut microbiota Gram-negative bacteria-generated endotoxin LPS leading to elevations in circulating LPS and metabolic endotoxemia and increased LPS endocytosis and intracellular LPS. Gram-negative bacteria promoted by HFD enter the bloodstream and enter cells which are mediated by GBPs to increase intracellular bacteria and LPS to activate caspase-11. Caspase-11 activation is triggered by its interaction with LPS from Gram-negative bacteria. Being an initiator caspase, activated caspase-11 functions primarily through its cleavage of key substrates. GSDMD is the primary substrate of caspase-11, and the GSDMD cleavage fragment generated (GSDMD-NT) leads to the formation of pores in the plasma membrane and secretion of caspase-1 produced IL-1B into the extracellular space to promote liver inflammation (NASH) and subsequently increased hepatic pyroptosis and promotes NAFLD. Thus, caspase-11 functions as an intracellular sensor for LPS and an immune effector. Palmitic acid produced by lipolysis in HFD-fed mice caspase-11 activation and GSDMD cleavage. Furthermore, LPS-induced caspase-11 activation and GSDMD cleavage also maintain dual fuel bioenergetics-glycolysis and OXPHOS and. Casp11–/– decreased GSMDM cleavage and IL-1β secretion, reduced liver inflammation, and hepatic pyroptosis.