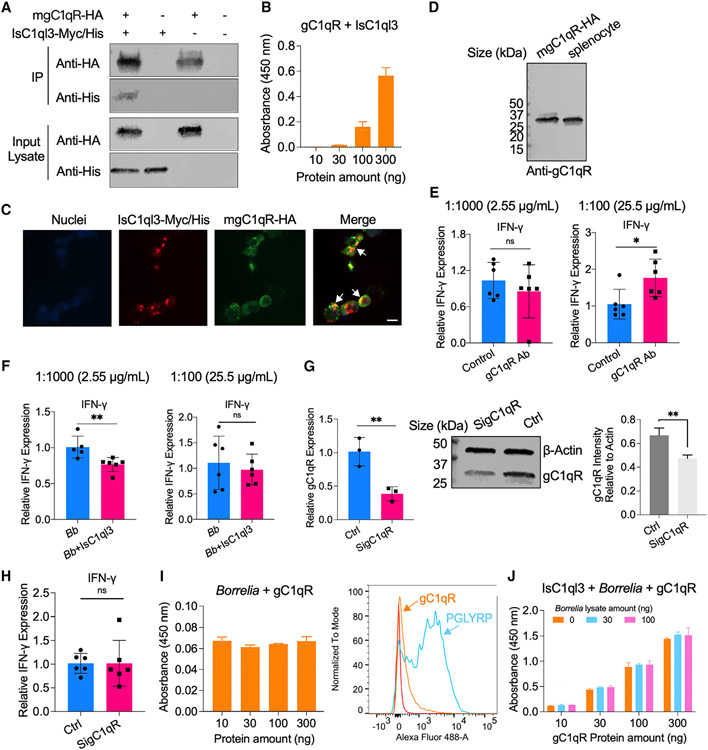
Figure 6. IsC1ql3 interacts with gC1qR on the surface of immune cells and modulates host immune responses.
(A) gC1qR-HA interacted with IsC1ql3-Myc/His in coIP assays with co-transfecting plasmids encoding mouse mgC1qR-HA and/or IsC1ql3-Myc/His into HEK293T cells.
(B) ELISA results show the interaction of IsC1ql3 and gC1qR. The rgC1qR protein was immobilized on microtiter wells and probed with increasing concentrations (10–300 ng) of rIsC1ql3 protein. rIsC1ql3 showed dose-dependent interaction with rgC1qR protein. Three biological replicates with three technical replicates were included in this assay. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(C) Co-immunolocalization of gC1qR-HA and IsC1ql3-Myc/His. gC1qR-HA was detected using a rabbit anti-HA polyclonal antibody and goat anti-rabbit IgG labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 (green) secondary antibody. IsC1ql3-Myc/His was detected using a mouse anti-His polyclonal antibody and goat anti-mouse IgG labeled with Alexa Fluor 549 (red) secondary antibody. The white arrows indicate examples of colocalization. Bar: 10 μm.
(D) gC1qR is expressed in the splenocytes as determined by western blot.
(E) The splenocytes were incubated with gC1qR antibody (Ab) at a concentration of 1:1,000 (2.55 μg/mL) and 1:100 (25.5 μg/mL). The IFN-γ gene expression was then evaluated by qPCR. The gC1qR polyclonal antibody stimulates IFN-γ gene expression at the concentration of 1:100. Each dot represents one biological replicate. Data are represented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was assessed using a non-parametric Mann-Whitney test (*p < 0.05; ns, p > 0.05).
(F) The splenocytes were incubated with 25.5 and 2.55 μg/mL gC1qR antibody for 20 min and then the cells were stimulated with a mixture of IsC1ql3 and B. burgdorferi. IFN-γ gene expression was then evaluated by qPCR. The polyclonal antibody against gC1qR blocked interactions with IsC1ql3 in splenocytes at the concentration of 1:100. Each dot represents one biological replicate. Data are represented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was assessed using a non-parametric Mann-Whitney test (**p < 0.01; ns, p > 0.05).
(G) gC1qR expression was silenced by delivering siRNA into splenocytes. qPCR and immunoblotting confirmed silencing of gC1qR. Control (Ctrl) group was transfected with Allstars negative control (Qiagen). Each dot represents one biological replicate. Data are represented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was assessed using an unpaired t test (**p < 0.01).
(H) Silencing of gC1qR affected IsC1ql3-mediated IFN-γ inhibition. Each dot represents one biological replicate. Data are represented as mean ± SD. Statistical significance was assessed using a non-parametric Mann-Whitney test (ns, p > 0.05).
(I) B. burgdorferi did not interact with gC1qR as determined by ELISA and flow cytometry. The peptidoglycan recognition protein 1 (PGLYRP1) was used as the positive control.38 Three biological replicates with three technical replicates were included in this assay. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(J) Competitive ELISA showed that the interaction between gC1qR and IsC1ql3 was not altered in the absence or presence of B. burgdorferi. The rIsC1ql3 protein with or without B. burgdorferi lysate was probed with increasing concentrations (10–300 ng) of gC1qR protein. Three biological replicates with three technical replicates were included in this assay. Data are represented as mean ± SD.