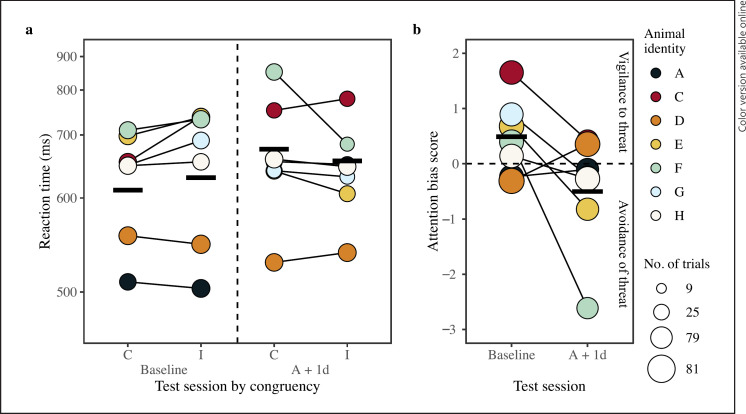
Fig. 3.
Investigating if monkeys' responses to congruent and incongruent trials and attention bias changed on the day immediately after prolonged anesthesia (A + 1d) for 100 ms trials. Data shown were taken at baseline and A + 1d. a Mean reaction time per monkey for the interaction of congruency and test session, connected by a thin black line. The dashed vertical line separates baseline data from A + 1d data. Note that responses by monkey A were similar to monkey H for the A + 1d test session; therefore, the data appear overlapped. b Mean attention bias score (mean response per monkey to incongruent trials subtracting that of congruent trials) per monkey for each test session (baseline, A + 1d). Positive values indicate a bias toward threatening content, whereas a negative value indicates a bias away from such content (separated by the dashed horizontal line). The point area indicates the number of trials per condition for reaction time data and the number of trials used to calculate the attention bias score per test session, ranging from 20 to 68 trials. The Y-axis of reaction time in plot (a) is scaled according to the transformed data; values of the Y-axis of the attention bias score in plot (b) are on the scale of 10 to the minus 5 power due to score being calculated using the transformed response. Model estimates are indicated by thick horizontal lines for each condition when all other predictors are at their mean (either dummy coded or z-transformed).