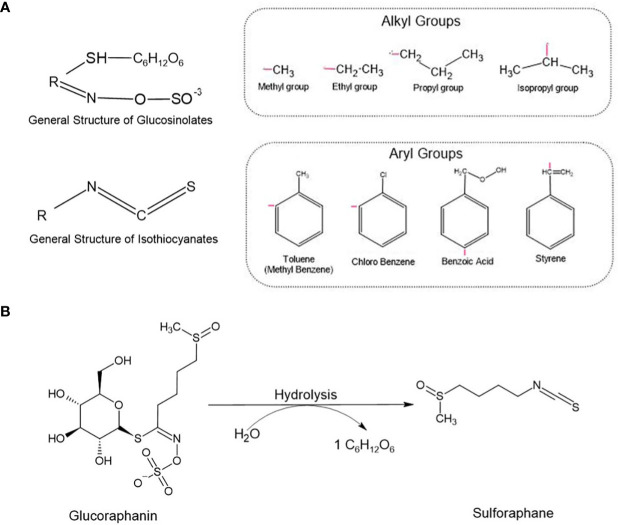
Figure 1.
(A) Glucosinolates and Isothiocyanates general structures. The radical ‘R’ represents different alkyl and aryl groups. (B) Glucoraphanin, a glucosinolate, is converted into sulforaphane (SFN) by the enzyme myrosinase. During the chemical reaction, glucoraphanin is hydrolyzed releasing a glucose molecule (C6H12O6) and resulting in the active form of SFN.