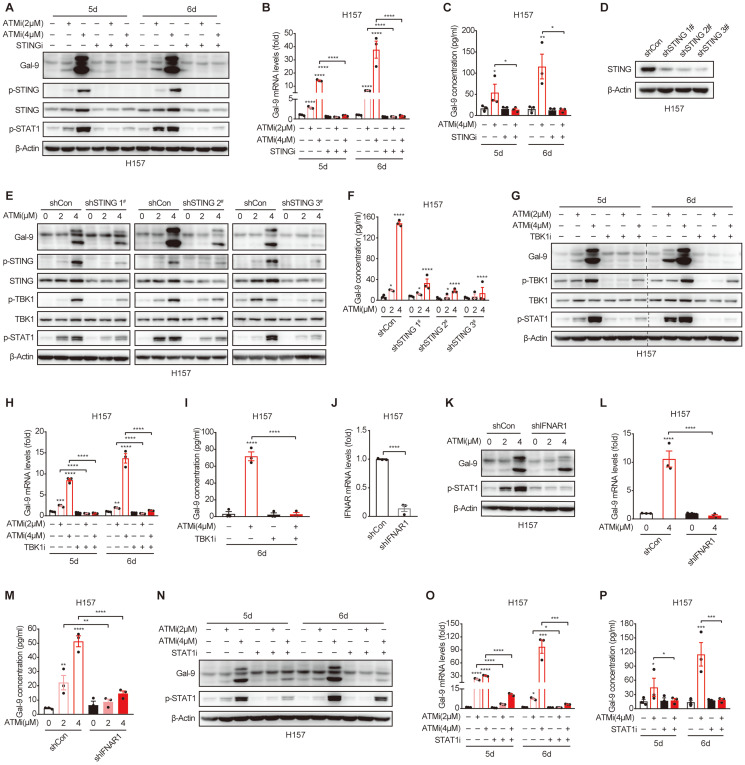
Figure 4.
Gal-9 induction by ATM inhibition is mediated by STING-IFNβ pathway. A-C. Immunoblot, RT-qPCR and ELISA analysis of Gal-9 in H157 cells concurrently treated with KU-60019 (2 μmol/L or 4 μmol/L) and STING inhibitor (H151, 10 μmol/L) for indicated time. D. Immunoblot analysis of Gal-9 in vector control and STING-KD H157 cells expressing three different STING shRNAs. E-F. Immunoblot and ELISA analysis of Gal-9 in vector control and STING-KD H157 cells treated with KU-60019 (2 μmol/L or 4 μmol/L) or DMSO (vehicle control) for 5 days. G-I. Immunoblot, RT-qPCR and ELISA analysis of Gal-9 in H157 cells concurrently treated with KU-60019 (2 μmol/L or 4 μmol/L) and p-TKB1 inhibitor (GSK8612, 5 μmol/L) for indicated time. J. RT-qPCR analysis of IFNAR1 in vector control and IFNAR1-KD H157 cells. K-M. Immunoblot, RT-qPCR and ELISA analysis of Gal-9 in vector control and IFNAR1-KD H157 cells treated with KU-60019 (2 μmol/L or 4 μmol/L) or DMSO (vehicle control) for 5 days. N-P. Immunoblot, RT-qPCR and ELISA analysis of Gal-9 in H157 cells concurrently treated with KU-60019 (2 μmol/L or 4 μmol/L) and p-STAT1 inhibitor (Fludarabine, 0.25 μmol/L) for indicated time. n.s., not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.