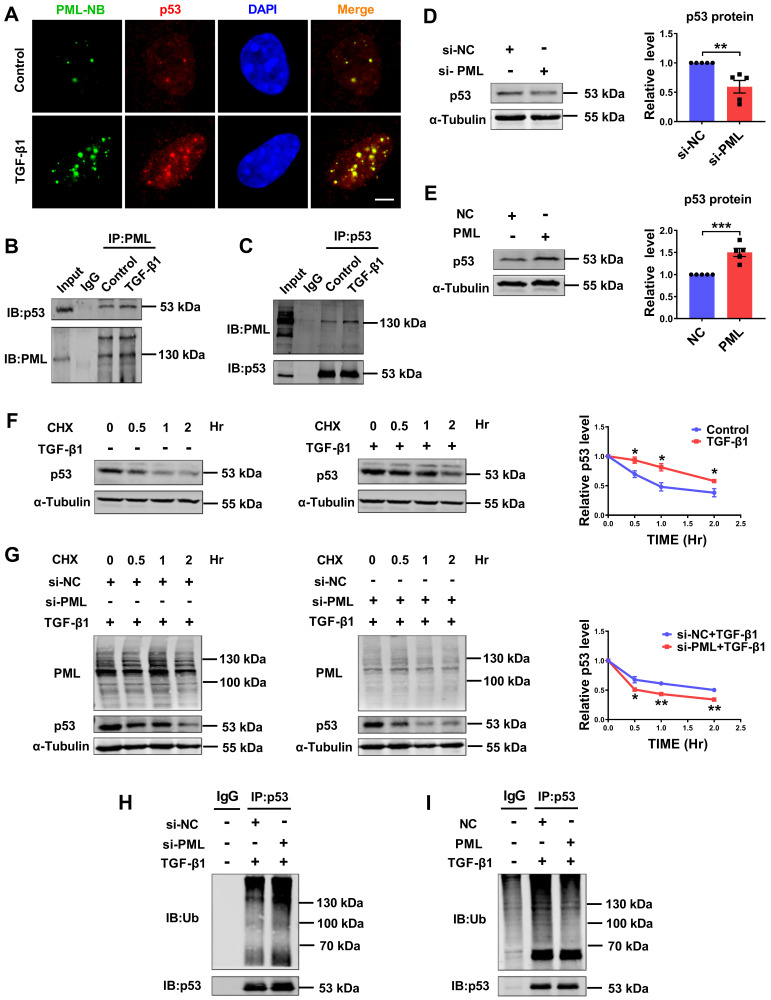
Figure 5.
PML stabilizes p53 by directly binding to p53 in response to TGF-β1. (A) Co-localization of PML and p53 was detected by immunofluorescence analysis in CFs after treatment with TGF-β1. Scale bar, 5 μm (n = 5). (B and C) Representative immunoblots showing of co-immunoprecipitated PML/p53 complexes in CFs treated with TGF-β1. Extracts of cells were immunoprecipitated with either anti-PML or anti-p53 antibodies and then were precipitated with either antibody (n = 5). (D) Analysis of the expression of p53 by western blot after transfection of si-PML (n = 5). (E) Analysis of the expression of p53 by western blot after transfection of PML plasmid (n = 5). (F) P53 protein levels were measured at different time points in CFs treated with cycloheximide (CHX) (10 μg/ml), CHX plus TGF-β1 by western blot analysis (n = 3). (G) PML knockdown accelerates the degradation of p53. Twenty-four hours after transfection with si-PML, CFs were incubated with CHX plus TGF-β1 for the indicated times (n = 3). (H and I) The anti-p53 antibody was used to immunoprecipitate p53-ubiquitin immunocomplexes, followed by IB analysis using the anti-Ub antibody in CFs transfected with si-PML or PML overexpression plasmid after treatment with TGF-β1 (n = 3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.