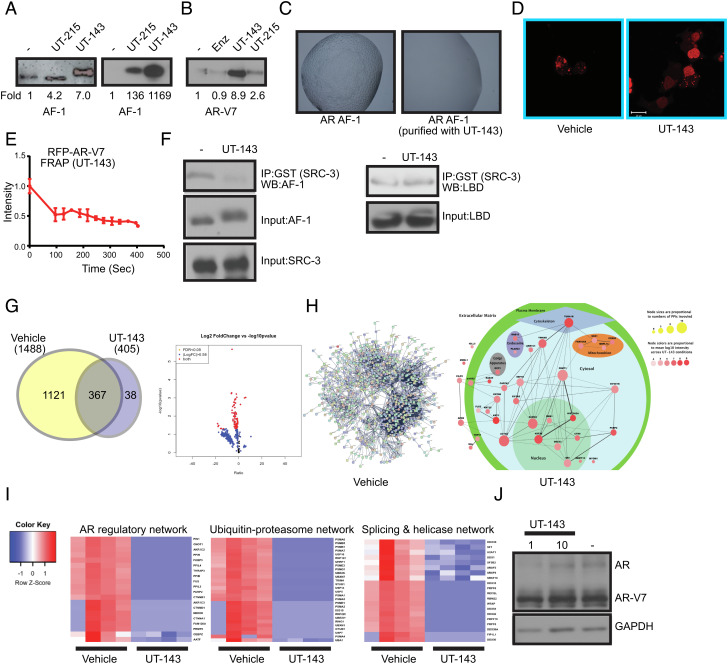
Fig. 3.
SARICA disrupts the disordered properties of AF-1 and AR-V7. (A) SARICAs stabilize AF-1 protein. (Left) Recombinant-purified AF-1 protein (5 ng) was incubated at room temperature for 4 h with DMSO or 50 µM of UT-143 and UT-215. Proteins were fractionated on an SDS-PAGE and western blot was performed with AR antibody (AR-441) that binds to the AF-1 region. The blots were quantified and expressed as fold change from vehicle controls. (Right) Bacterial cells expressing the AF-1 plasmid in the absence or presence of 30 µM UT-215 or UT-143 (added at the time of protein synthesis induction with 1 mM IPTG). Protein was purified and the purified protein (5 ng) was incubated at room temperature for 4 h. The proteins were fractionated on an SDS-PAGE and western blotted with AR-441 antibody. The blots were quantified and expressed as fold change from vehicle controls. (B) SARICAs stabilize AR-V7. Recombinant-purified AR-V7 protein (5 ng) was incubated at room temperature for 4 h in the absence or presence of 50 µM of the indicated compounds. Proteins were fractionated on an SDS-PAGE and western blot for AR-V7 was performed. The blots were quantified and expressed as fold change from vehicle controls. (C) UT-143 inhibits LLPS formation. AR AF-1 protein grown in the absence or presence of 30 µM UT-143 was incubated in the buffer shown in Fig. 1D. The LLPS formed was imaged using a microscope. (D) UT-143 dissolves AR-V7 condensates. COS7 cells were transfected with 1 µg turbo red RFP-AR-V7 and treated in DME + 10% FBS 24 h after transfection with vehicle or 10 µM UT-143 for 24 h. Cells were imaged using confocal microscope 24 h after treatment. (E) UT-143 blocks mobility of AR-V7. Photobleaching was performed in live cells that were treated with vehicle or 10 µM UT-143 and the recovery was monitored and graphed as described in Fig. 1F. Average and SE of n = 4 regions are presented. (F) UT-143 disrupts AF-1-coactivator interaction, but not AF-2-coactivator interaction. An equal amount of recombinant-purified AF-1 protein (Left) or AR LBD (Right) was incubated at 4 °C with DMSO or 100 µM UT-143 for 2 h and then incubated overnight at 4 °C with GST-tagged SRC-3-purified protein. The complex was immunoprecipitated with GST antibody and western blotted with AR-441 (for AF-1) or AR-C19 antibody (for LBD). Input controls show no change in the level of any protein. Representative experiment is presented here. (G–I) RIME assay. 22RV1 cells plated in DME + 10%FBS were treated with DMSO or 10 µM UT-143 for 16 h (n = 4/IP). Cells were fixed and the RIME assay was performed with AR-V7 of IgG antibody, and the protein complex (AR-V7 complex subtracted from IgG) detected by mass spectrometry. The data are represented as Venn diagram (G), volcano plot (G), and interacting proteins mapping (H). (I) Heatmap of selected pathways. (J) UT-143 does not change AR and AR-V7 protein expression. 22RV1 cells plated in DME + 10% FBS were treated as indicated under the RIME assay, and western blot for AR and AR-SV with an NTD-recognizing antibody was performed.