Fig. 1.
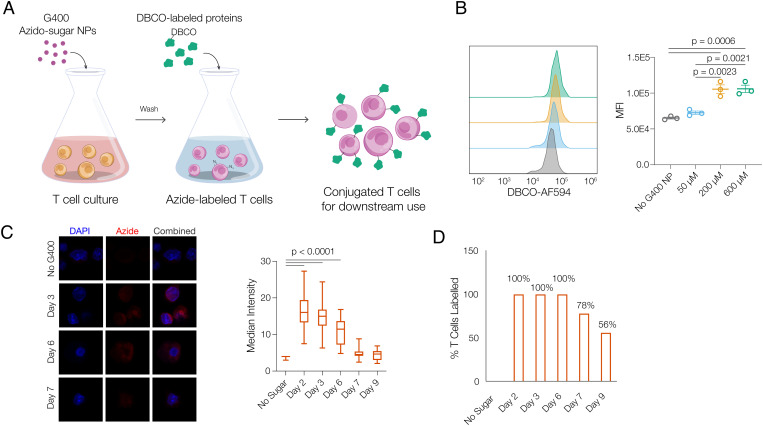
Azido-sugar nanoparticles metabolically label T cells with cell-surface azide groups. A, Schematic of metabolic labeling and cytokine conjugation of T cells with azido-sugar G400 NPs. Azido-sugar nanoparticles are directly added to T cell culture, enter T cells via endocytosis, and lead to presentation of azide group on T cell surfaces. After T cells are metabolically labeled, T cells are washed and DBCO-labeled proteins (e.g., cytokines) are directly added to produce conjugated T cells for downstream use. B, Median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of T cell surface azide signals after T cells are treated with G400 NPs at various concentrations for 3 d (n = 3, one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test). C, Representative fluorescent imaging and quantification of maintenance of azide signal from T cells, and (D) percentage of T cells with positive azide signal over time. T cells were treated with 200 µM G400 NP for 3 d, after which G400 NP in the medium was removed (day 0) and T cells were subsequently cultured free of G400 NP (one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test).