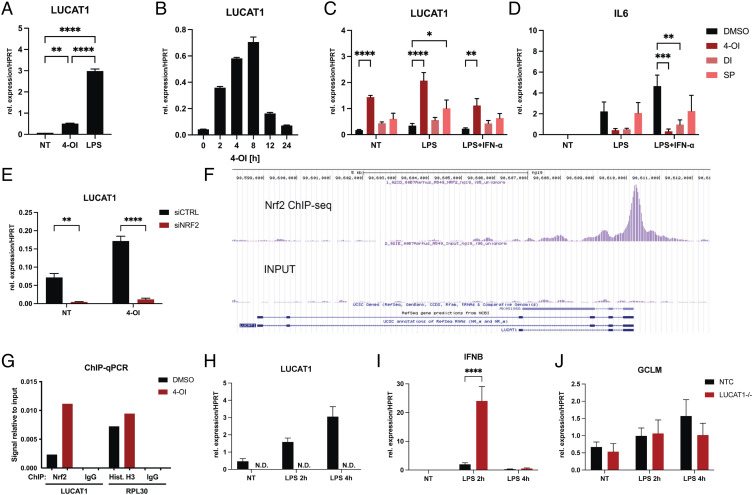
Fig. 1.
LUCAT1 is induced by 4-octyl itaconate through an NRF2-dependent mechanism. (A and B) qPCR analysis of LUCAT1 expression in moDCs treated for 2 h with 100 µM 4-octyl itaconate (4-OI) or 200 ng/mL LPS in A and with 100 µM 4-OI for 0 to 24 h in B. Data are from three (A) or two (B) different healthy donors. (C and D) qPCR analysis of LUCAT1 (C) and IL6 (D) expression in moDCs pre-treated with 250 µM 4-OI, 250 µM di-methyl itaconate (DI) or 5 µM sulforaphane (SP) for 4 h before stimulated with 200 ng/mL LPS +/−10 ng/mL IFN-α 2b. Data are from three to four different healthy donors (n = 3 to 4). (E) qPCR analysis of LUCAT1 expression in MDMs pre-treated with control siRNA or siRNA for NRF2 and stimulated with 4-OI. Data are from three different healthy donors (n = 3). (F) ChIP-seq results from A549 cells for NRF2 in LUCAT1 locus. (G) ChIP-qPCR results from THP-1 cells showing amplification of LUCAT1 or RPL30 promoter region after pulldown with NRF2, Histone H3 or IgG control antibody precipitation. (H–J) qPCR analysis of LUCAT1 (H), IFNB (I), GCLM (J) expression in THP-1 control guide RNA (NTC) or LUCAT1−/− cells after stimulation with 200 ng/mL LPS for 2 or 4 h. Data are from four independent experiments (n = 4). (A–H) Data are represented as mean ± SEM. P values (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001) have been determined by one-way ANOVA in A or two-way ANOVA in C–H. NT: not treated; N.D.: not detectable.