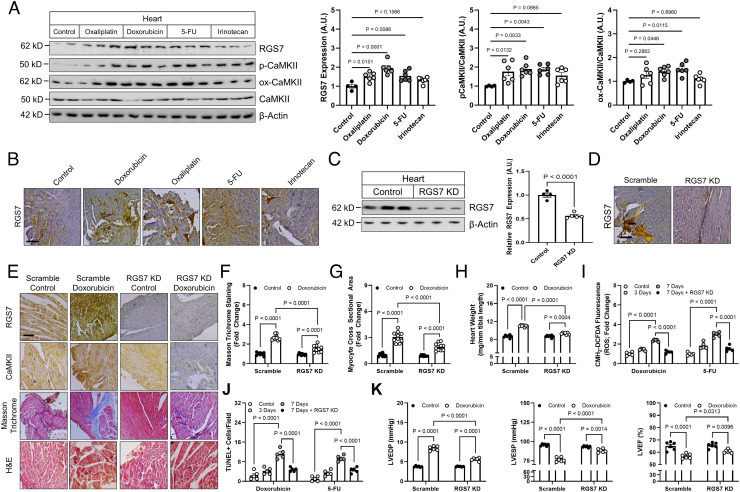
Fig. 4.
Cardiac-specific RGS7 knockdown ameliorates chemotherapy-dependent cardiotoxicity in mice. (A–H, K) Following administration of scramble or RGS7-shRNA via intracardiac injection, mice were treated with doxorubicin (cumulative dose of 45 mg/kg i.p.), 5-FU (200 mg/kg i.p.), oxaliplatin (45 mg/kg i.p.), irinotecan (175 mg/kg i.p.), or saline control. After 8 wk, cardiac phenotyping was performed, and tissues collected 1 wk later for biochemical and histological analyses. (A) Immunoblotting for RGS7, p-CaMKII, and ox-CaMKII in heart (n = 6). (B) RGS7 immunohistochemistry in heart. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) RGS7 knockdown was verified in heart via (C) immunoblotting and (D) immunohistochemistry. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) (E) Representative images depicting RGS7, CaMKII, Masson trichrome (fibrosis), and H&E staining (myofibrillar architecture) in mice. (Scale bar, 100 μm.) Quantification of (F) fibrotic area (blue stain) from Masson trichrome (n = 10) and (G) myocyte area from H&E images (n = 10). (H) Heart weight (n = 10). (I and J) Mice were treated with single acute dose of doxorubicin (20mg/kg, i.p.), 5-FU (150 mg/kg, i.p.), oxaliplatin (30 mg/kg, i.p.), or saline control. (I) CM-H2-DCFDA fluorescence (ROS; n = 5). (J) Quantification of TUNEL+ nuclei (apoptosis; n = 5). (K) Cardiac phenotyping (n = 6); left ventricular end diastolic and systolic pressure and LVEF.