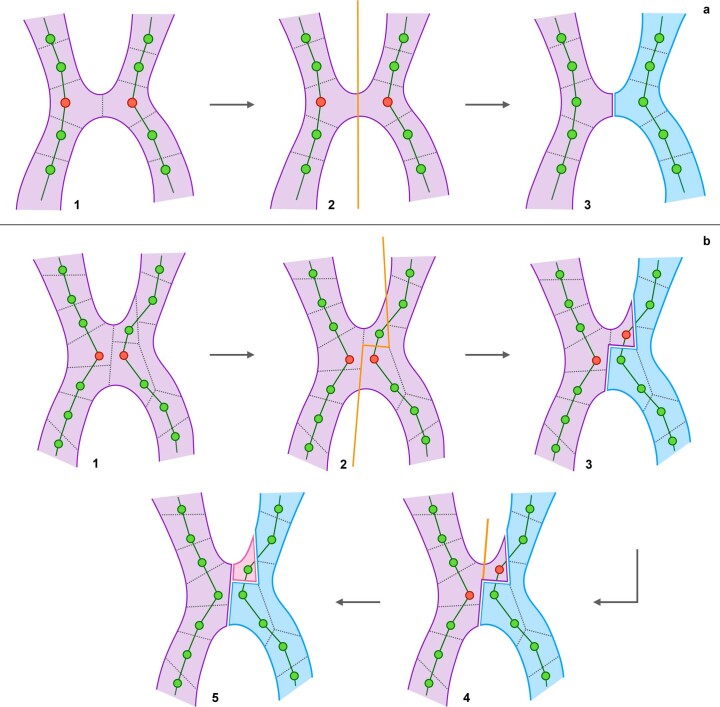
Extended Data Fig. 1. Overview of the proposed MCM.
Overview of the proposed MCM. A. Simple case. Two ground-truth skeletons are contained inside an erroneously merged segment. Dashed lines represent supervoxel boundaries and the closest skeleton nodes need to be split to resolve the merge (1). A min-cut is performed (2), resulting in a new segment (3). B. Complex case. Two skeletons are contained in a falsely merged segment as before (1), but the supervoxels are more fragmented. A min-cut is performed (2), resulting in a new segment (3). However, two nodes contained within the original segment need to be split. A second min-cut is performed (4), which produces another segment (5). This results in an additional split error caused by the original cut.