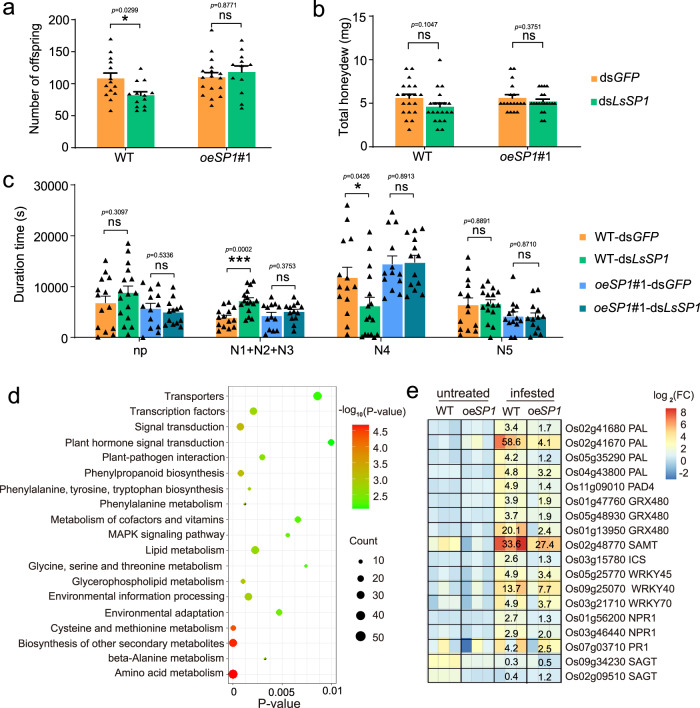
Fig. 5. Influences of Laodelphax striatellus infestation on wild type (WT) and oeSP1#1 plants.
a–c Comparison of fecundity (a), honeydew excretion (b), and electrical penetration graph (EPG) parameters (c) between dsGFP-treated and dsLsSP1-treated L. striatellus on WT and oeSP1#1 plants. P-values were determined by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns, not significant. Data are presented as mean values ±SEM. For fecundity (a) and honeydew (b) analysis, n = 20 independent biological replicates in each treatment; for EPG analysis (c), n = 14 (WT-dsGFP), n = 16 (WT-dsLsSP1), n = 13 (oeSP1#1-dsGFP), and n = 13 (oeSP1#1-dsLsSP1) independent biological replicates. All EPG recordings were performed for 8 h. N1 + N2 + N3 pathway duration, N4 phloem sap ingestion, N5 xylem sap ingestion, np nonpenetration. d Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis of DEGs specifically identified in WT plants, but not in oeSP1#1 plants. Enriched P-values were calculated according to one-sided hypergeometric test using TBtools software70. e The impacts of L. striatellus infestation on salicylic acid (SA) marker genes in WT and oeSP1#1 plants. PAL phenylalanine ammonia lyase, PAD4 phytoalexin deficient 4, GRX480 glutaredoxin GRX480, SAMT SA methyl transferase, ICS isochorismate synthase, WRKY transcription factor WRKY, NPR1 non-repressor of pathogenesis-related protein 1, PR1 pathogenesis-related 1, SAGT SA glucosyl transferase. Nipponbare rice plants and transgenic plants of Nipponbare background were used. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.