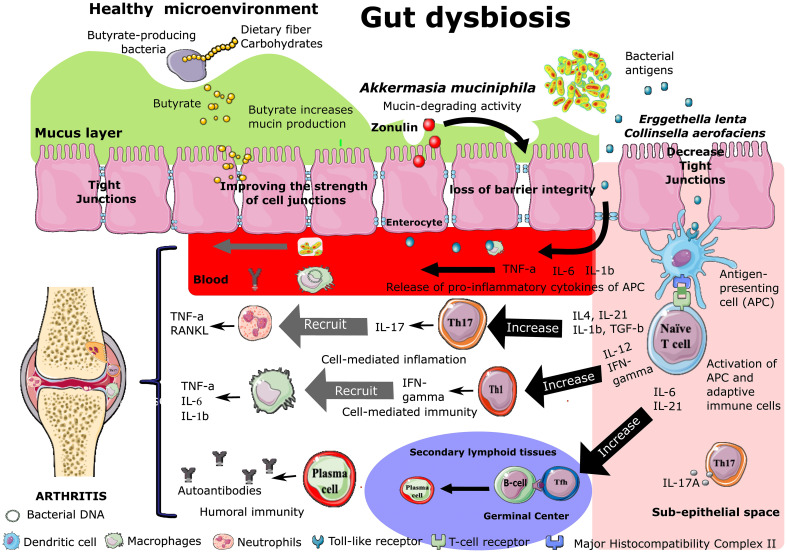
Figure 2.
Effect of intestinal dysbiosis on intestinal permeability and B and T cell polarization during the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Increased Zonulin secretion is followed by increased intestinal permeability (“leaky gut”) associated with the disassembly of ZO-1 protein from the tight junction complex. Bacteria or their components are transported to the joints via secondary lymphoid organs or the bloodstream. After encountering the microbiota-derivated antigen presented by antigen-presenting cells (APCs), naive CD4+ T cells differentiate into various subsets, including at least Th1, Th17, and Tfh cells.