Figure 1.
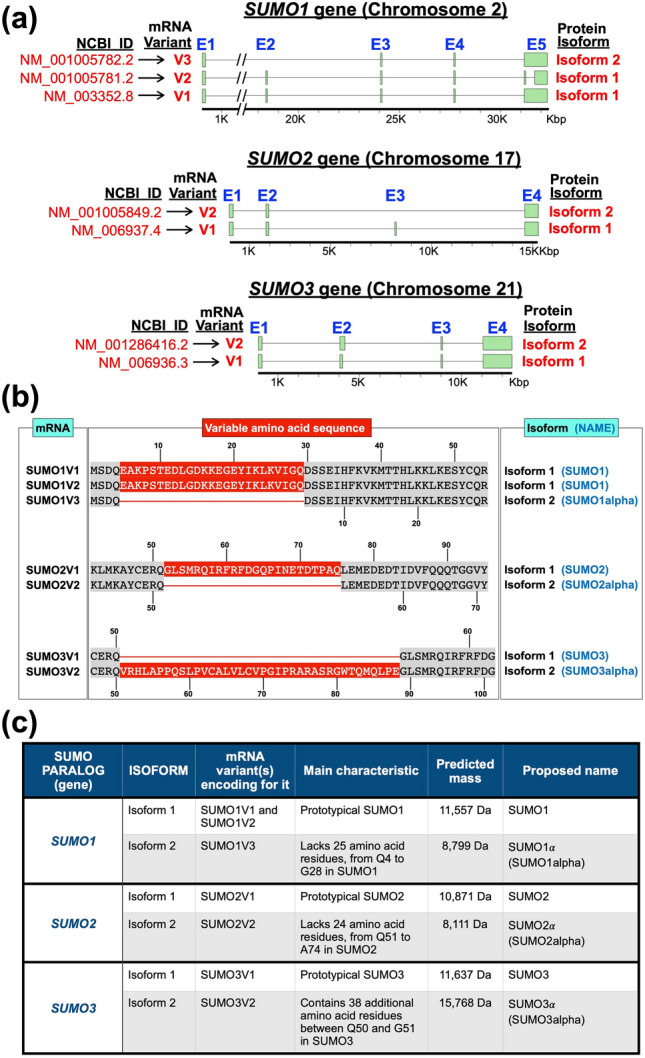
Predominant variant forms of the mature mRNAs coding for the three main SUMO paralogs in humans, according to current NCBI RNA-sequencing data. (a) Schematic of the SUMO1, SUMO2, and SUMO3 genes, showing the distribution of exons (E) (green rectangles) and introns (connecting lines) along the genes and the different transcripts produced by normal and alternative splicing. The bars at the bottom represent the gene, with residues from the transcriptional start site indicated in thousands of base pairs (Kbp). The NCBI identifier and name given to each variant are indicated to the left (in red) and the protein isoform encoded by each variant is indicated to the right. In every case, isoform 1 is the prototypical SUMO protein. (b) Schematic emphasizing the specific amino acid differences (shown in red) between the proteins encoded by the normally spliced mRNA variants and the alternatively spliced ones. The numbers on top indicate the amino acid residue in the prototypical SUMO isoform (isoform 1), whereas the numbers at the bottom indicate the amino acid residues in the alternative protein isoforms, which are thereafter referred to as the SUMO alpha isoforms. (c) Summary of the properties of the different protein isoforms encoded by each SUMO paralog, including their proposed names, the specific transcript variant(s) coding for them, and their main features.
