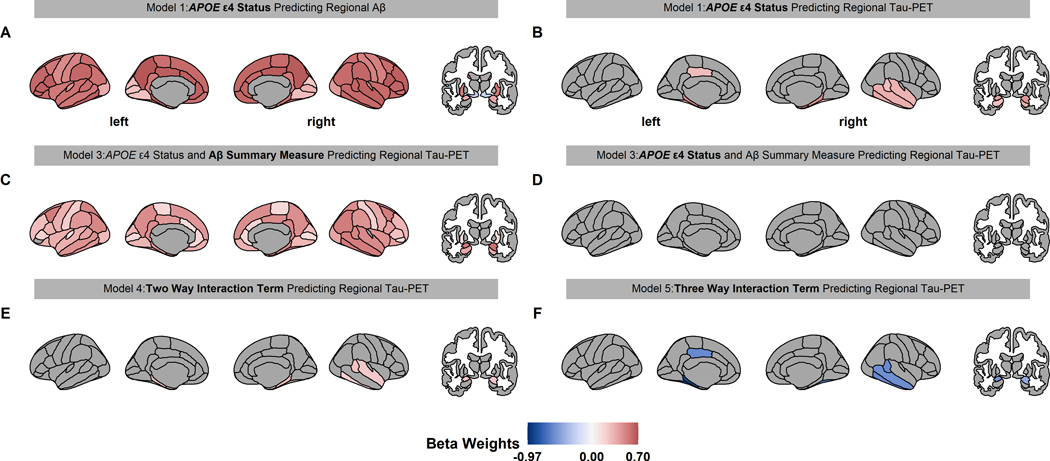
Fig 1.
Significant beta weights predicting regional Aβ and tau PET for linear models 1–5. The associated linear model is displayed above each brain with the beta weight term in bold text. Red and blue color indicate a positive and negative value, respectively. Only the regions that were statistically significant in figures 1A and B (conjunction) were analyzed in E and F. Aβ PET is increased throughout the brain in APOE ε4 carrier (A). APOE ε4 carriers have higher tau PET in the temporal, amygdala, and hippocampus regions (B). When APOE ε4 carrier status and Aβ PET were both in a model predicting regional tau PET, the Aβ summary measure was associated with tau PET throughout the brain (C), but APOE ε4 carrier status was not associated with tau PET (D). Importantly, the interaction between Aβ summary measure and APOE ε4 carrier status in predicting regional tau PET were significant in the entorhinal, temporal, and amygdala regions (E) and this potentiation varies by sex (F).