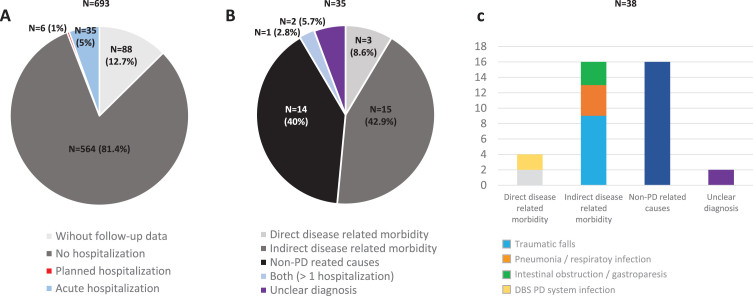
Fig. 2.
A) Percentage of PD patients from the COPPADIS cohort (N = 693; 1 excluded due to change in the diagnosis) without follow-up data (N = 88; 12.7%), without hospitalization (N = 564; 81.4%), with planned hospitalization (N = 6; 1%), and with acute hospitalization (N = 35; 5%) during the 1-year follow-up after the baseline visit. B) Percentage of patients with at least one acute hospitalization (N = 35) regarding the reason of admission: Direct PD-related morbidity (N = 3; 8.6%); Indirect PD-related morbidity (N = 15; 42.9%); Non-PD related causes (N = 40; 40%); More than 1 hospitalization with both reasons (N = 1; 2.8%); Unclear diagnosis (N = 2; 5.7%). C) Reasons for hospital admissions (38 events) in the subgroup of patients with acute hospitalization: 1) Direct PD-related morbidity (4 events; 10.5%); 2) Indirect PD-related morbidity: traumas, pneumonia, and intestinal obstruction / gastroparesis (16 events; 42.1%); 3. Non-PD related causes (16 events; 42.1%). PD, Parkinson’s disease.