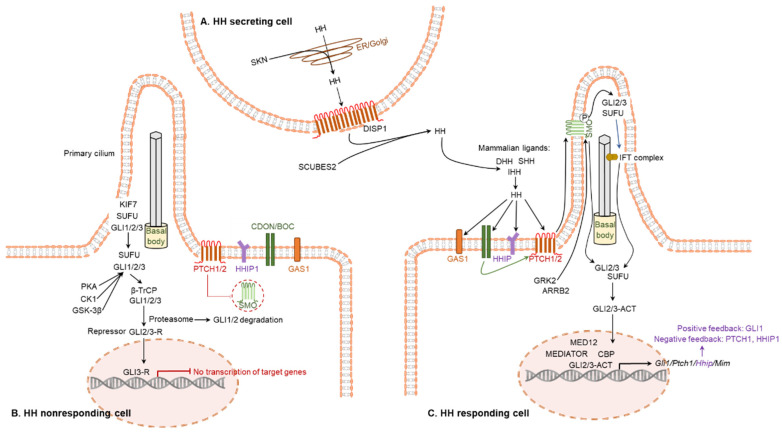
Figure 4.
Canonical hedgehog signaling pathway. (A) The active form of HH molecules are secreted from the HH expressing cells. (B) In the absence of HH ligand, PTCH inhibits SMO. This is associated with GSK-3β, CK1, and PKA-mediated phosphorylation of GLI, which forms a truncated form of GLI repressor. The repressor GLI translocates to the nucleus in order to inhibit the transcription. (C) Active form of HH ligand binds to PTCH receptor on the responding cells and the HH ligand-dependent interaction with PTCH and SMO results in release of SMO activator. SMO controls the processing of GLI factors, activate GLI, and initiate the cascade of downstream signaling pathways. Activated GLI translocates to the nucleus and initiates the transcription of HH target genes.