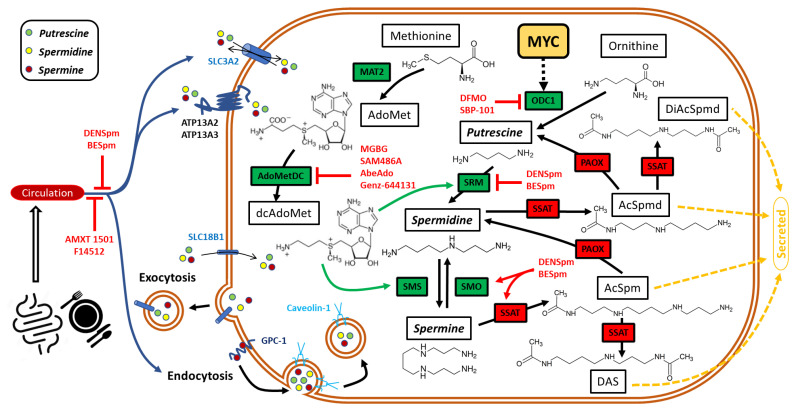
Figure 1.
Biosynthesis, metabolism, transport, and targeting of polyamines. (1) Polyamine biosynthesis: ornithine is generated from arginine and converted into putrescine by ornithine decarboxylase (ODC1). Spermidine synthase (SRM) turns putrescine into spermidine, which is further converted into spermine by spermine synthase (SMS). Synthesis of spermidine and spermine requires aminopropyl moiety from decarboxylated S-adenosylmethionine (dcAdoMet), which is converted from S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) by S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase (AdoMetDC). AdoMet is produced from methionine by methionine adenosine transferase (MAT). (2) Polyamine catabolism: spermidine and spermine are decomposed by spermidine/spermine-N1-acetyltransferase (SSAT) into N-acetylspermidine (AcSpmd) and N-acetylspermine (AcSpm), respectively. AcSpmd and AcSpm are further catabolized by acetylpolymine oxidase (PAOX) into spermidine and putrescine, respectively. In addition, spermine oxidase (SMOX) specifically degrades spermine into spermidine. (3) Polyamine transport: exogenous sources of polyamines, including foods and gut microbiota. Uptake of polyamines from the gut may be mediated by caveoline-1- and NOS-2-dependent processes. Solute carrier transporter SLC3A2 imports putrescine. At the cellular level, heparan sulfate proteoglycans glypican-1 (GPC-1) sequesters spermine for its uptake, likely through endocytosis. Caveoline-1-dependent endocytosis mediated polyamine uptake from extracellular compartments. SLC3A2 can either import or export polyamines following their concentration gradient. SLC18B1 promotes polyamine exocytosis in mast cells but is also required for polyamine uptake in the brain. ATP13A2 and ATP13A3 are involved in polyamine internalization via poorly characterized mechanism(s). (4) Targeting polyamine pathways: polyamine analogs or small molecule inhibitors targeting the polyamine metabolism pathway antagonize the tumor-promoting activities of polyamines. Small molecules AMXT 1501, F14512, and polyamine analogs DENSpm and BESpm block the uptake of polyamines by cancer cells. In addition, DENSpm and BESpm also inhibit polyamine synthesis by suppressing SRM or promote polyamine catabolism by upregulating SMOX and SSAT. DFMO and SBP-101 repress ODC, while MGBG, SAM486A, AbeAdo, and Genz-644131 target AMD to downregulate polyamine synthesis.