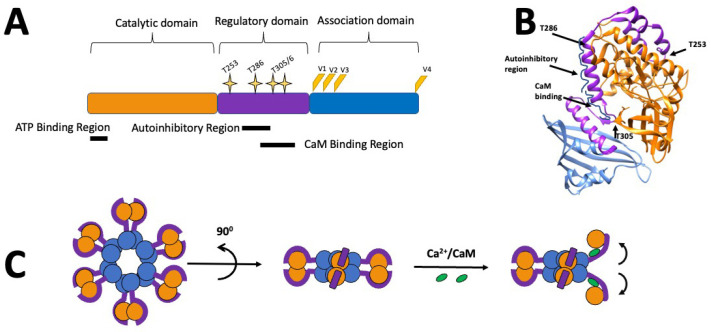
Figure 1.
Schematic representations of the molecular structure of CaMKIIα: (A) CaMKII consists of a catalytic domain (orange), a regulatory domain (purple), which includes overlapping autoinhibitory and calmodulin (CaM) binding regions and multiple phosphorylation sites (yellow stars). The association domain (blue) is involved in the formation of CaMKII multimers. Splice sites (V1–4) are represented in orange/yellow. (B) Crystal structure (3SOa) of a single CaMKIIα subunit created using Chimera [44]. (C) Representation of the CaMKIIα holoenzyme structure, with the domains shown in the same colours as in (A), and showing the movement of the subunit and its catalytic domain following activation with calcium/calmodulin.