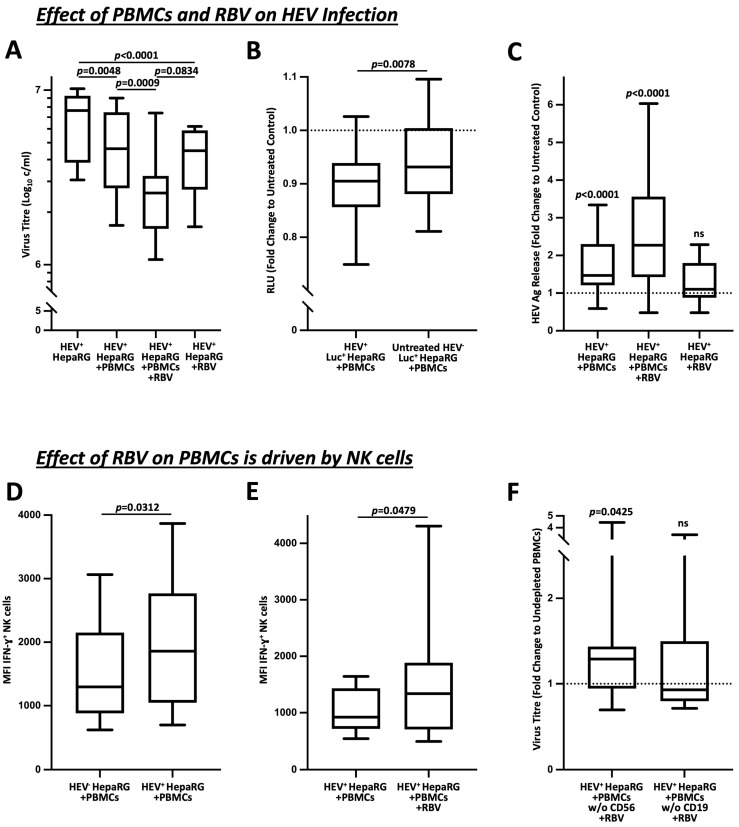
Figure 1.
Immunomodulation of RBV boosts the antiviral effect of NK cells. (A) demonstrates the effect of RBV on PBMCs in HEV+ HepaRG co-culture represented by alteration in viral loads (n = 24). (B) shows the change of luciferase activity as indication for HepaRG viability in sole presence of PBMCs. The corresponding setups without co-culture of PBMCs acted as the untreated controls (n = 39). (C) pictures the quantification of HEV antigen concentrations from co-culture supernatants in relation to untreated controls (n = 24). (D,E) show the effects of co-culture of PBMCs with infected target cells and RBV treatment on IFN-γ production by NK cells upon IL-12/IL-15 stimulation (n = 6 and n = 13). (F) illustrates the effect of CD56 depletion on antiviral activity by PBMCs in the context of RBV treatment (n = 26). Appearance: median with interquartile range (whiskers min to max), statistical analysis: Friedman test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test (A), Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test (B,D,E) or one-sample Wilcoxon signed-rank test (C,D).