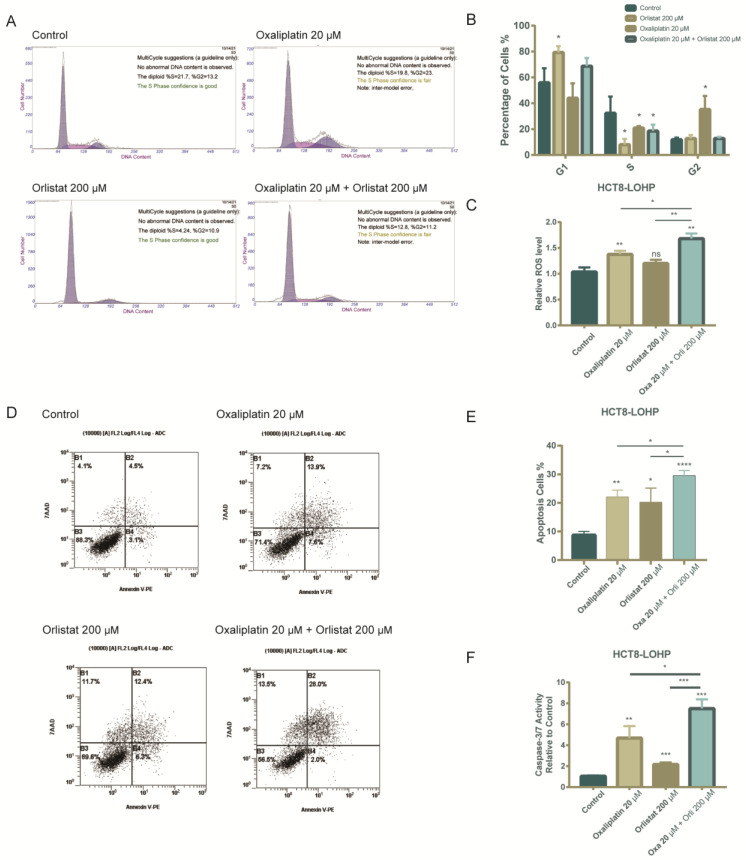
Figure 4.
Oxaliplatin combined with Orlistat induced cell-cycle arrest and increased ROS levels and apoptosis in HCT8-LOHP cell lines. (A,B) Cell-cycle analysis by flow cytometry indicated that treatment with oxaliplatin, Orlistat, and drug combination led to G1 arrest. Additionally, the change in each phase of cell cycle in each group was analyzed by one-way ANOVA with the Dunnett post hoc test. (C) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) was evaluated using the Reactive Oxygen Species Assay Kit (Beyotime). The result indicated that combination of Orlistat and oxaliplatin significantly increased ROS levels in HCT8-LOHP cell lines. (D,E) Apoptosis level, indicated by staining cells with Annexin V/7-AAD in each group in indicated treatments, was compared with control by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test, respectively. (F) Cellular caspase-3/7 activity was determined by the Caspase 3/7 Activity Apoptosis Assay Kit *Green Fluorescence (Sangon Biotech) and expressed relative to the control. Cells were treated for 72 h. Relative caspase activity upon indicated treatments was compared with the control by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001, ns: no significance.