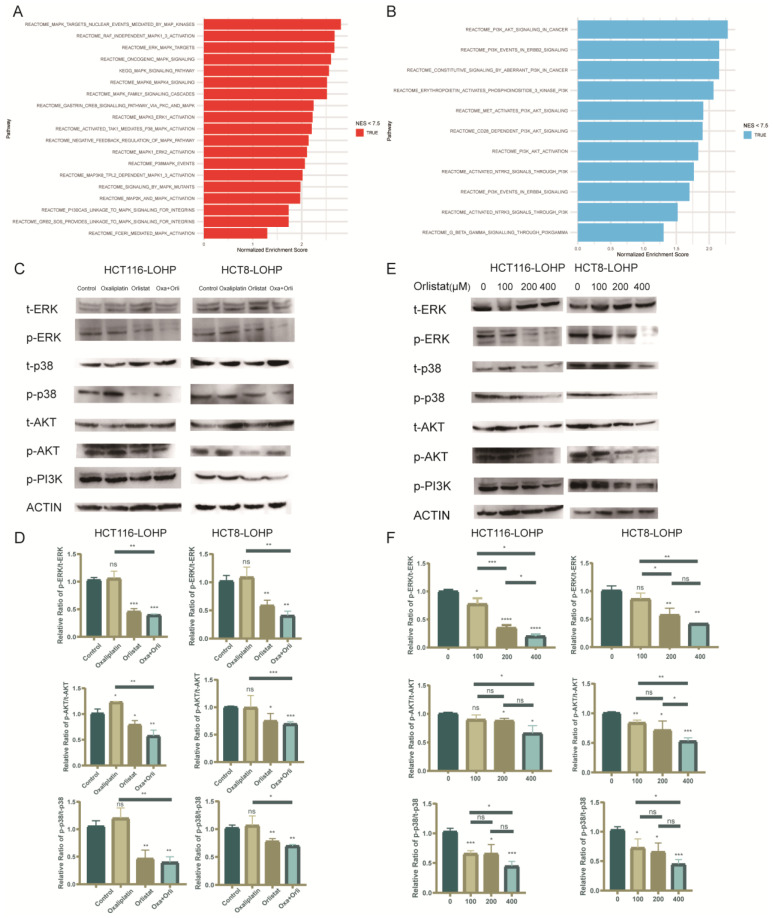
Figure 5.
Phosphorylation of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways was involved in the process by which Orlistat enhances anti-proliferation effect of oxaliplatin. (A,B) Genome-wide RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis was performed on HCT8-LOHP cells. Gene ontology (GO) analysis compared untreated cells with Orlistat treatment schemes and depicted the most significant change in signaling pathways. Compared with cell lines treated with Orlistat, MAPK/ERK (A) and PI3K/AKT (B) pathways were activated more. (C,D) There was a distinct change in phosphorylation of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways in cell lines exposed to oxaliplatin, Orlistat, and both. Western blot analysis depicted that whether oxaliplatin was utilized or not, Orlistat could inhibit phosphorylation of MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways. Relative intensity ratio of each band on western blot see Table S2. (E,F) Under 20 µM oxaliplatin treatment, phosphorylation levels in 116-LOHP and HCT8-LOHP cell lines decreased with increasing concentration gradients of Orlistat. Relative intensity ratio of each band on western blot see Table S3. The uncropped blots are shown in Figure S5. * p ≤ 0.05, ** p ≤ 0.01, *** p ≤ 0.001, **** p ≤ 0.0001, ns: no significance.